In today’s digital age, LED displays have become an integral part of how we communicate visually. From towering billboards in Times Square to the screens on our smartphones, LED technology powers the vibrant and dynamic images that capture our attention. But what exactly is an LED display, how does it work, and why has it become the preferred choice for so many applications? This comprehensive article delves into the world of LED displays, explaining their technology, advantages, types, and practical uses.
Understanding LED Display Technology
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. LED displays use thousands, sometimes millions, of these tiny diodes arranged in a matrix to create images and videos. Unlike traditional display technologies such as LCD or plasma, LEDs produce their own light, which leads to superior brightness and contrast.
The core principle behind an LED display is simple: each pixel on the screen is made up of one or more LEDs that emit red, green, and blue light. By varying the intensity of these three colors, the display can produce millions of different hues, enabling rich and vibrant images. This RGB color mixing is fundamental to all color LED displays.
Modern LED displays are typically classified as either direct-view LED or LED-backlit LCD. Direct-view LED displays use LEDs as the actual pixels, while LED-backlit LCDs use LEDs as a light source behind an LCD panel. This article focuses primarily on direct-view LED displays, which are widely used in large-format screens and outdoor signage.
How LEDs Work in Displays
Each LED in a display is a tiny semiconductor chip that emits light when electrons recombine with holes within the device. The color of the light depends on the materials used in the semiconductor. For displays, red, green, and blue LEDs are combined to form a single pixel. By adjusting the current flowing through each LED, the display controls the brightness and color output.
This precise control allows LED displays to achieve high dynamic range and color accuracy. The ability to turn off individual LEDs completely results in true blacks, which contributes to the high contrast ratios that LED displays are known for.
Advantages of LED Displays Over Other Technologies
LED displays offer several significant advantages compared to older or alternative display technologies, making them the preferred choice for many applications.
Superior Brightness and Visibility
One of the most notable benefits of LED displays is their exceptional brightness. LEDs can produce light at intensities far beyond what LCD or plasma screens can achieve. This makes LED displays ideal for outdoor use where sunlight can wash out less bright screens. For example, outdoor digital billboards using LED technology can reach brightness levels of 5,000 to 8,000 nits, ensuring clear visibility even in direct sunlight.
Energy Efficiency and Longevity
LEDs are inherently energy-efficient because they convert a higher percentage of electricity into light rather than heat. This efficiency translates into lower operating costs, especially for large installations that run continuously. Additionally, LEDs have a longer lifespan than traditional bulbs or display technologies, often lasting upwards of 100,000 hours before significant degradation occurs.
Flexibility and Scalability
LED displays can be manufactured in virtually any size or shape, from small wearable screens to massive stadium displays covering thousands of square feet. Their modular design allows for easy scalability and maintenance. Panels can be seamlessly tiled together to create ultra-large displays without visible seams, a feature highly valued in arenas, concerts, and public spaces.
High Refresh Rates and Fast Response Times
LED displays offer high refresh rates and fast response times, which are crucial for video playback and dynamic content. This reduces motion blur and flicker, providing a smooth viewing experience. For applications like sports broadcasting or gaming, where fast-moving images are common, LED displays outperform many other technologies.
Types of LED Displays and Their Applications
LED display technology has diversified into various types, each suited for specific environments and uses. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right display for a particular application.
Indoor LED Displays
Indoor LED displays are designed for environments with controlled lighting and typically have higher pixel densities for close viewing distances. These displays are common in retail stores, conference rooms, airports, and control centers. Pixel pitches (the distance between individual LEDs) for indoor displays usually range from 0.8mm to 4mm, allowing for high-resolution images that look sharp even from a few feet away.
For example, a corporate lobby might use an indoor LED video wall to showcase branding and promotional content, taking advantage of the display’s vivid colors and brightness without overwhelming viewers.
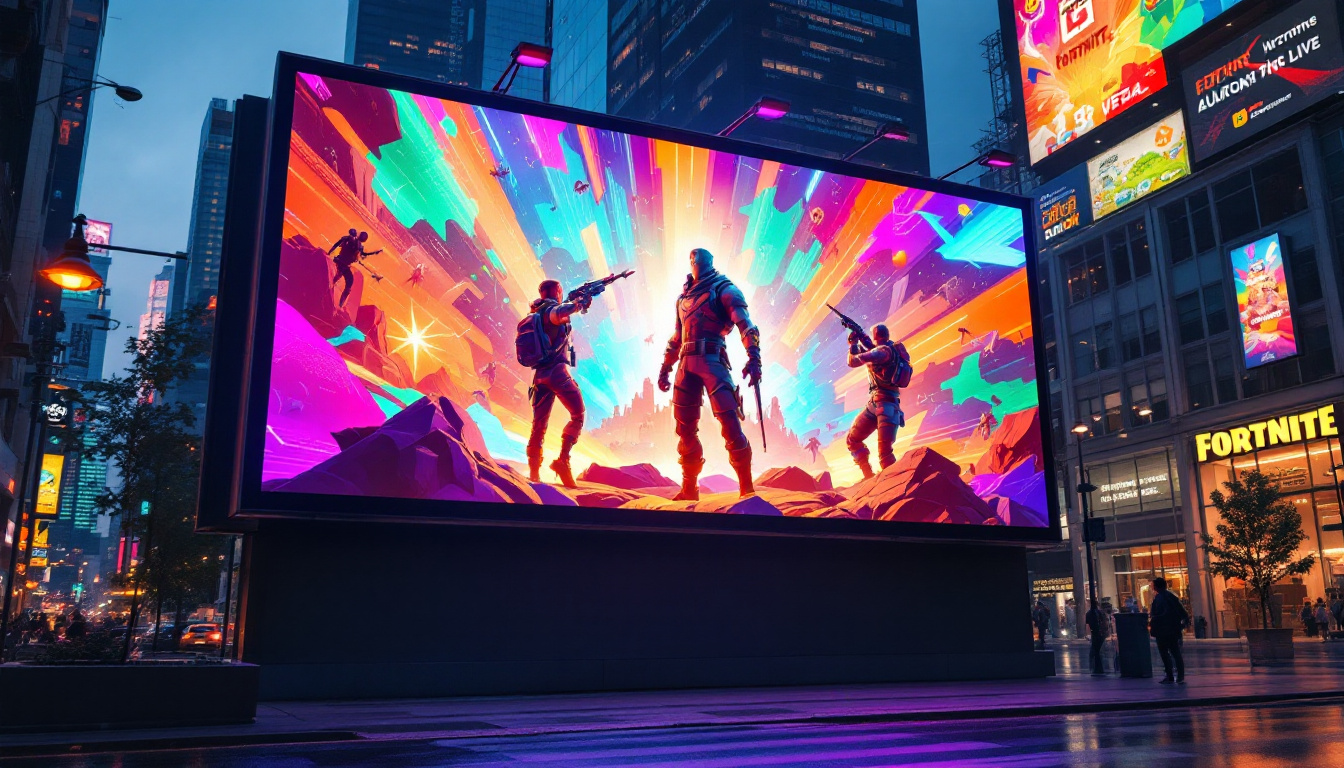
Outdoor LED Displays
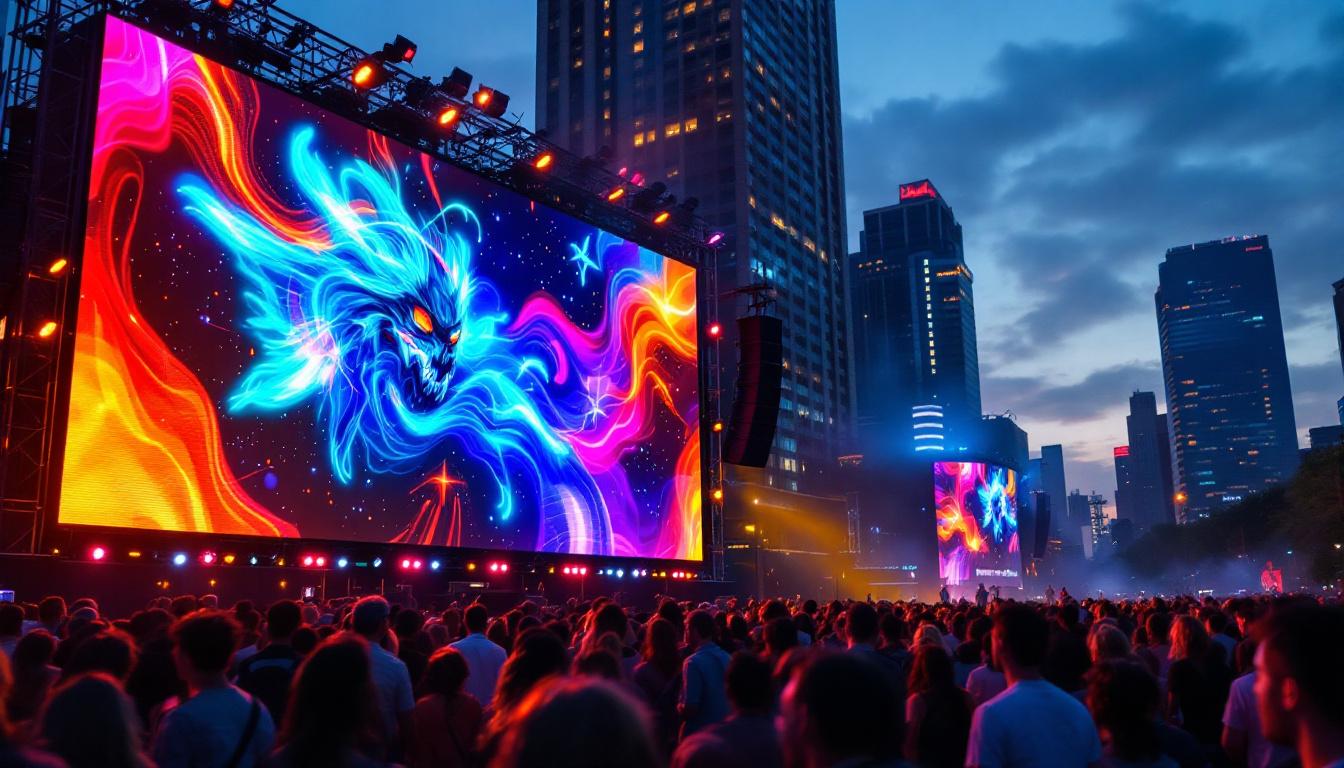
Outdoor LED displays are built to withstand harsh weather conditions and deliver high brightness to combat sunlight glare. These displays often have larger pixel pitches, typically between 4mm and 20mm, since they are viewed from greater distances. Common applications include digital billboards, stadium screens, transportation signage, and public information displays.
One notable example is the massive LED screens in Times Square, New York City, which use outdoor LED technology to create dazzling advertisements visible from blocks away.
Transparent LED Displays
Transparent LED displays are an innovative variation where the LEDs are embedded in a transparent substrate, allowing viewers to see through the screen. These are used in retail storefronts, museums, and architectural installations to combine digital content with physical environments seamlessly.
For instance, luxury stores often use transparent LED displays on glass windows to attract customers with dynamic visuals while still allowing natural light and visibility inside the store.
Flexible and Curved LED Displays
Advances in LED technology have enabled the creation of flexible and curved LED panels. These displays can wrap around surfaces or form cylindrical shapes, opening new possibilities for creative installations and immersive experiences.
Concert venues and event organizers frequently use flexible LED displays to create engaging stage backdrops that conform to unique shapes, enhancing the visual impact of performances.
Key Considerations When Choosing an LED Display
Selecting the right LED display involves evaluating several factors to ensure optimal performance and return on investment.
Pixel Pitch and Resolution
Pixel pitch is a critical specification that determines the resolution and clarity of the display. Smaller pixel pitches mean higher resolution and better image quality, especially at close viewing distances. However, smaller pixel pitches also increase the cost of the display.
For example, a retail store with close-up viewing might opt for a 1.5mm pixel pitch display, while a highway billboard viewed from hundreds of feet away might use a 10mm pixel pitch.
Brightness and Contrast Ratio
Brightness is measured in nits, and the required level depends on the installation environment. Outdoor displays need much higher brightness to remain visible in sunlight. Contrast ratio, the difference between the darkest and brightest parts of an image, affects image depth and realism. LED displays typically offer excellent contrast due to their ability to turn off individual pixels completely.
Durability and Weather Resistance
For outdoor installations, the display must be weatherproof and resistant to dust, moisture, and temperature extremes. Look for displays with an IP (Ingress Protection) rating that matches the environmental conditions. For instance, an IP65 rating indicates protection against dust and water jets, suitable for most outdoor applications.
Viewing Angle and Distance
LED displays have wide viewing angles, often up to 160 degrees horizontally and vertically, ensuring visibility from various perspectives. However, the optimal viewing distance depends on pixel pitch and display size. Careful planning ensures that the audience experiences the intended image quality without pixelation or blurriness.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in LED Displays
The LED display industry continues to evolve rapidly, driven by advancements in materials, manufacturing, and software integration.
MicroLED Technology
MicroLED is an emerging display technology that uses microscopic LEDs to create even higher resolution and brightness with improved energy efficiency. Unlike OLEDs, MicroLEDs do not suffer from burn-in issues and can achieve superior longevity. While still in the early stages of commercialization, MicroLED displays promise to revolutionize everything from smartphones to large-format screens.
Integration with AI and IoT
Smart LED displays are increasingly integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. This enables dynamic content adaptation based on audience demographics, weather conditions, or real-time data inputs. For example, digital signage in shopping malls can change advertisements based on foot traffic patterns detected by sensors.
Energy Harvesting and Sustainability
As sustainability becomes a priority, manufacturers are developing LED displays with lower power consumption and recyclable materials. Some installations incorporate solar panels to offset energy use, particularly for remote or outdoor displays.
Practical Applications of LED Displays
LED displays have transformed numerous industries by enabling dynamic and engaging visual communication.
Advertising and Marketing
Digital billboards and video walls are now standard tools for advertisers aiming to capture attention in crowded urban environments. The ability to update content remotely and display high-impact visuals makes LED displays invaluable for marketing campaigns.
Sports and Entertainment
Stadiums and arenas use massive LED screens to enhance the spectator experience, showing live game footage, replays, and interactive content. Concerts and festivals employ LED backdrops to create immersive environments that complement performances.
Transportation and Public Information
LED displays provide critical information in airports, train stations, and bus terminals. Their high visibility and reliability ensure passengers receive timely updates on schedules, delays, and safety announcements.
Corporate and Education
Businesses and educational institutions use LED video walls for presentations, digital signage, and collaboration spaces. The clarity and flexibility of LED displays support effective communication and engagement.
Conclusion
LED display technology has revolutionized the way visual content is delivered across numerous sectors. Its combination of brightness, flexibility, energy efficiency, and durability makes it an ideal choice for both indoor and outdoor applications. As innovations like MicroLED and AI integration continue to develop, LED displays will become even more versatile and impactful.
Understanding the fundamentals of LED displays, from how they work to the factors influencing their performance, empowers businesses and organizations to make informed decisions when investing in this technology. Whether for advertising, entertainment, or information dissemination, LED displays offer a powerful medium to captivate audiences and communicate effectively.
Discover LumenMatrix’s Advanced LED Solutions
Ready to elevate your visual communication with cutting-edge LED technology? Explore LumenMatrix’s comprehensive range of LED display solutions, designed to captivate and engage your audience. From vibrant Indoor and Outdoor LED Wall Displays to dynamic Vehicle and Sports LED Displays, each product is crafted to deliver unparalleled clarity and impact. Embrace innovation with our Custom, All-in-One, and Transparent LED Displays, and see how our commitment to excellence can transform your brand’s visibility. Check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today and join the revolution in visual storytelling.