In the world of modern technology, the term SMD LED has become increasingly prevalent, especially in the realm of display technology. Understanding what an SMD LED is and how it works can provide valuable insights into various applications, from televisions to digital billboards. This article aims to demystify SMD LEDs, exploring their characteristics, advantages, and applications.
Understanding SMD LEDs
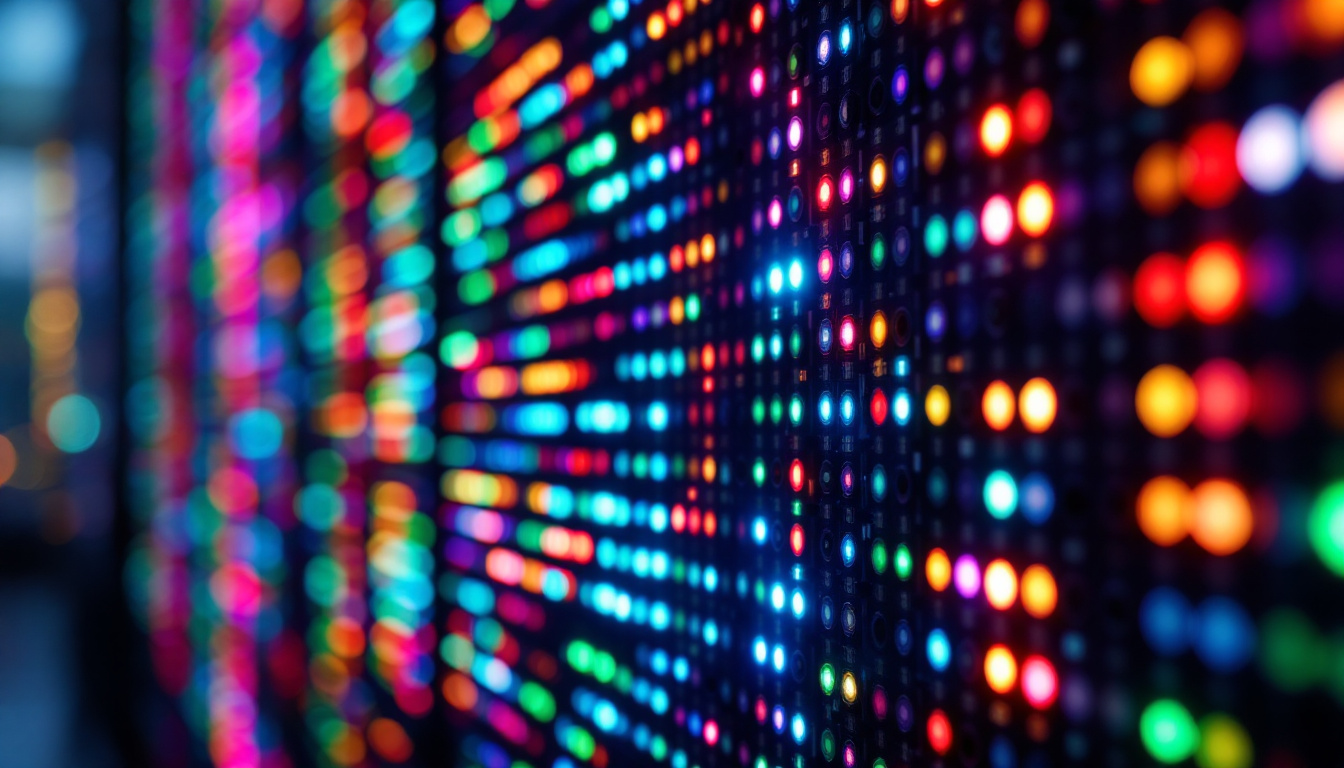
SMD stands for Surface-Mount Device, which refers to a type of LED that is mounted directly onto the surface of a circuit board. Unlike traditional through-hole LEDs, which require holes to be drilled into the circuit board, SMD LEDs are soldered onto the surface, allowing for a more compact and efficient design. This mounting technique not only saves space but also enhances the thermal management of the device, as the heat generated can dissipate more effectively across the surface of the board.
Construction and Design
The construction of an SMD LED typically involves a small chip of semiconductor material, usually made from gallium nitride or gallium phosphide, which emits light when an electric current passes through it. This chip is encased in a plastic housing, which not only protects the LED but also helps in diffusing the light emitted. The encapsulation material is often chosen for its optical properties, ensuring that the light output is maximized while minimizing losses due to reflection or absorption.
The design of SMD LEDs allows for a variety of configurations, including different colors and brightness levels. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from simple indicator lights to complex displays. Additionally, the small size and low profile of SMD LEDs enable innovative designs in modern electronics, allowing manufacturers to create thinner devices without compromising on performance. As technology advances, the integration of SMD LEDs into flexible circuit boards is becoming increasingly common, paving the way for new applications in wearable technology and flexible displays.
Types of SMD LEDs
There are several types of SMD LEDs, each designed for specific applications. The most common types include:
- Standard SMD LEDs: These are used in general lighting and display applications.
- High-Power SMD LEDs: Designed for applications requiring higher brightness, such as automotive lighting.
- RGB SMD LEDs: Capable of producing multiple colors by combining red, green, and blue light, making them popular in decorative lighting and displays.
In addition to these, there are also specialized SMD LEDs such as UV LEDs, which are used in applications like sterilization and curing processes, and smart LEDs that can be controlled via wireless technology for dynamic lighting solutions. The development of smart SMD LEDs has opened up new possibilities in home automation and energy-efficient lighting systems, allowing users to customize their lighting environments easily. As the demand for energy-efficient and versatile lighting solutions continues to grow, SMD LEDs are poised to play a crucial role in the future of illumination technology.
Advantages of SMD LEDs
The popularity of SMD LEDs can be attributed to several advantages they offer over traditional lighting solutions. These benefits are not only technical but also practical, making SMD LEDs a preferred choice in various industries.
Space Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of SMD LEDs is their compact size. Because they are mounted directly onto the surface of a circuit board, they take up less space than traditional LEDs. This space efficiency allows for more LEDs to be integrated into a single display, resulting in higher resolution and better image quality. Additionally, the compact nature of SMD LEDs enables their use in a variety of applications, from intricate electronic devices to large-scale displays, without compromising on performance. This versatility has led to their widespread adoption in everything from smartphones to large outdoor billboards, showcasing their ability to deliver vibrant visuals in constrained spaces.
Energy Efficiency
SMD LEDs are known for their energy efficiency. They consume significantly less power compared to incandescent and fluorescent lights, making them an environmentally friendly option. This energy efficiency translates into lower electricity bills and a reduced carbon footprint, which is increasingly important in today’s eco-conscious world. Moreover, their ability to emit light without generating excessive heat means that they not only save energy but also contribute to a cooler environment, reducing the need for additional cooling systems in indoor settings. As industries and consumers alike seek sustainable solutions, SMD LEDs stand out as a beacon of innovation, helping to drive the transition towards greener lighting technologies.
Longevity and Durability
Another compelling advantage of SMD LEDs is their longevity. Typically, SMD LEDs can last up to 50,000 hours or more, depending on usage conditions. This durability means less frequent replacements, which not only saves money but also reduces waste. Additionally, SMD LEDs are less susceptible to breakage compared to traditional glass bulbs, making them ideal for use in environments where durability is crucial, such as in automotive lighting or outdoor installations. Their robust design also allows them to perform reliably under a wide range of temperatures and conditions, ensuring consistent lighting performance over time. This resilience further solidifies their role as a dependable choice for both commercial and residential applications, where longevity and reliability are paramount.
Applications of SMD LEDs
The versatility of SMD LEDs allows them to be used in a wide range of applications across various industries. From consumer electronics to large-scale advertising displays, SMD LEDs have proven to be an invaluable technology.
Consumer Electronics
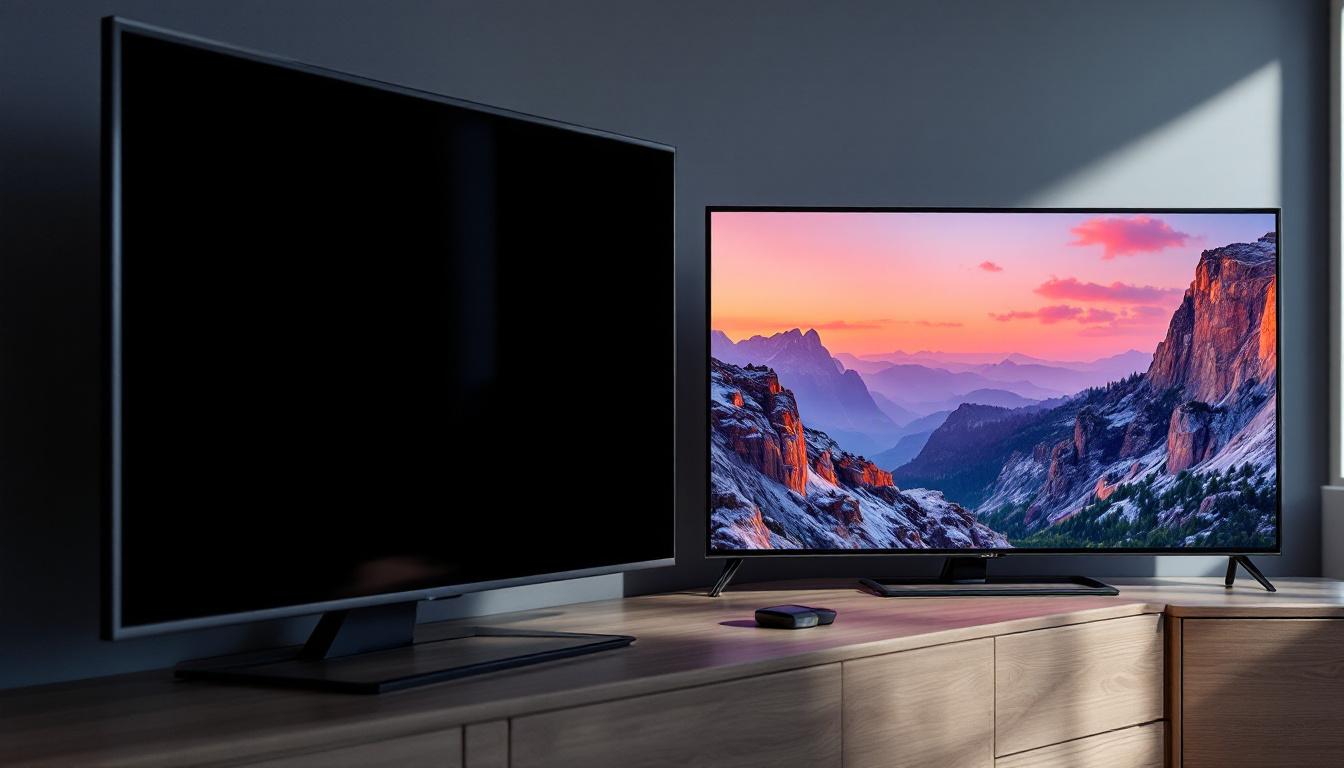
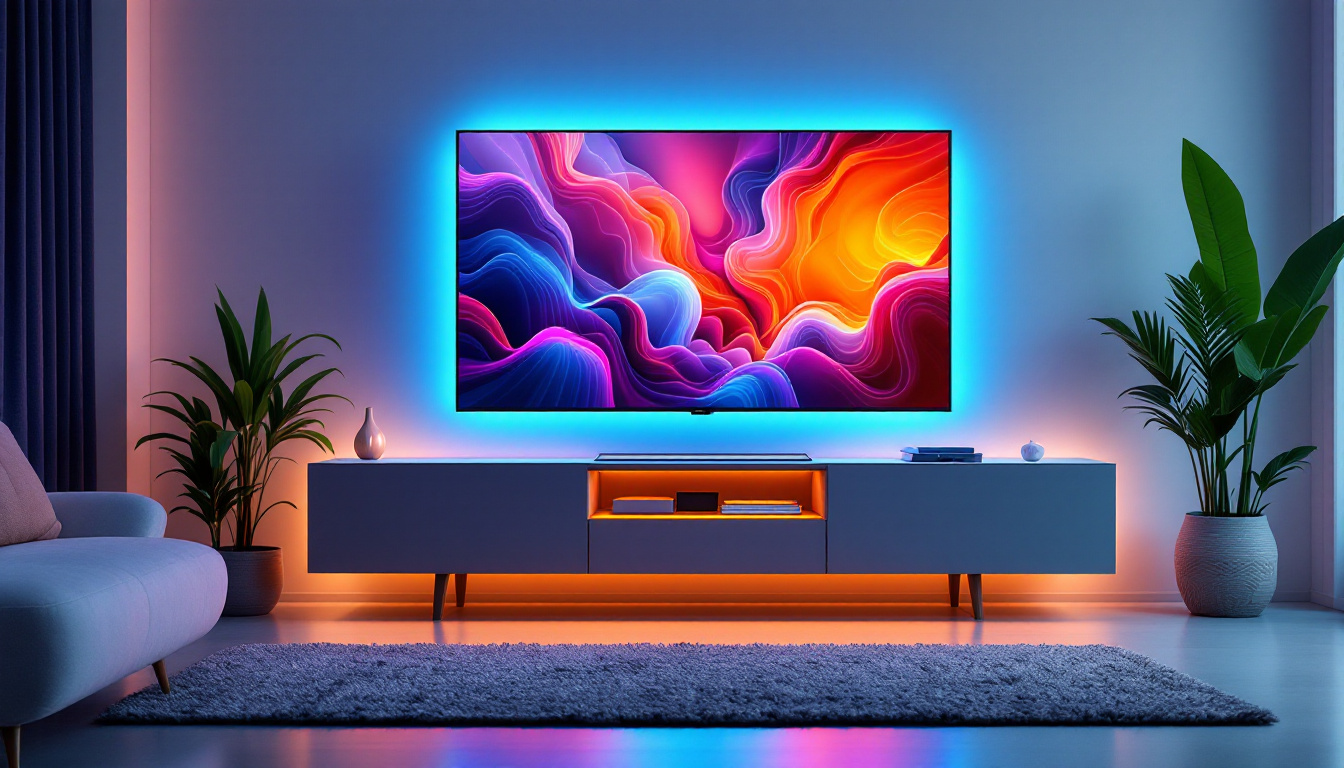
SMD LEDs are commonly found in consumer electronics, such as televisions, smartphones, and computer monitors. Their ability to produce bright, vibrant colors and high contrast ratios makes them ideal for display screens. Additionally, their compact size allows manufacturers to create thinner and lighter devices. This has led to the development of ultra-slim TVs and portable gadgets that not only look sleek but also offer enhanced performance. Furthermore, advancements in SMD LED technology have enabled features like HDR (High Dynamic Range) and 4K resolution, providing users with an immersive viewing experience that was previously unattainable with older display technologies.
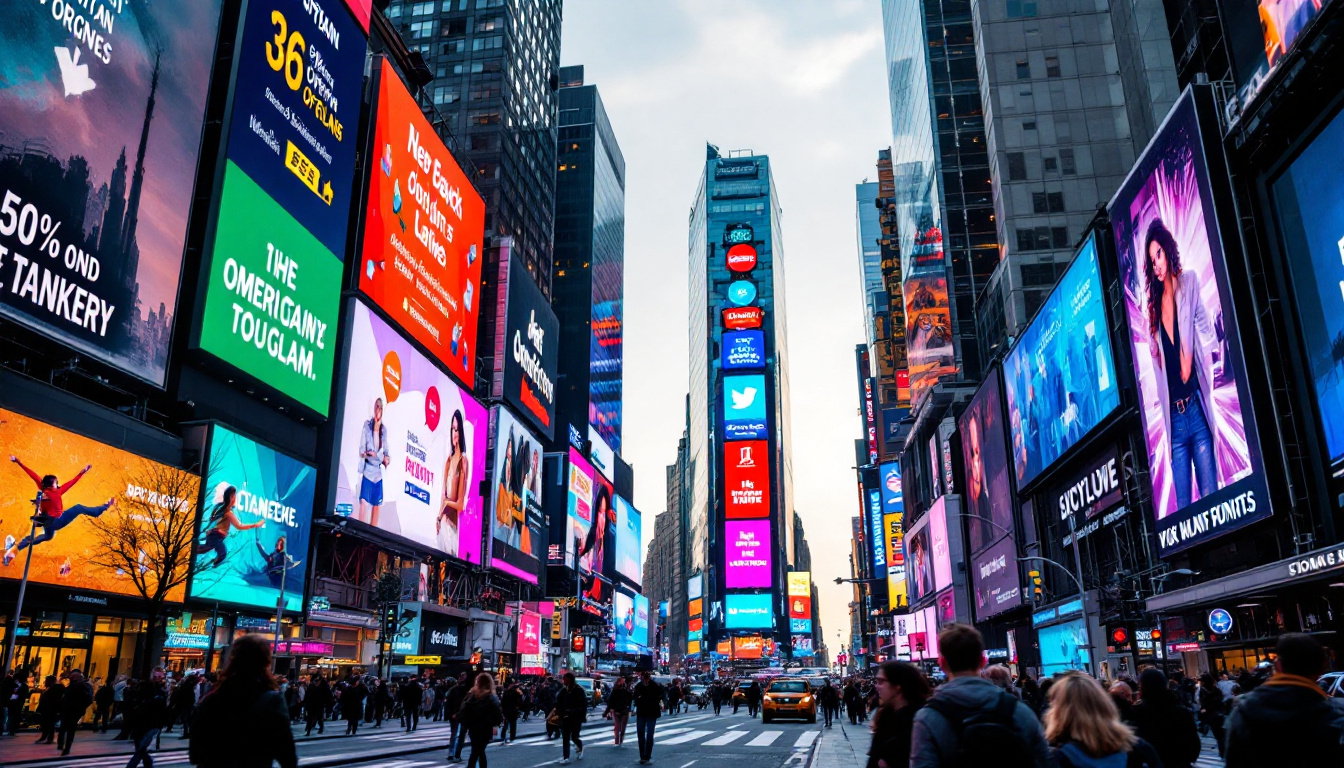
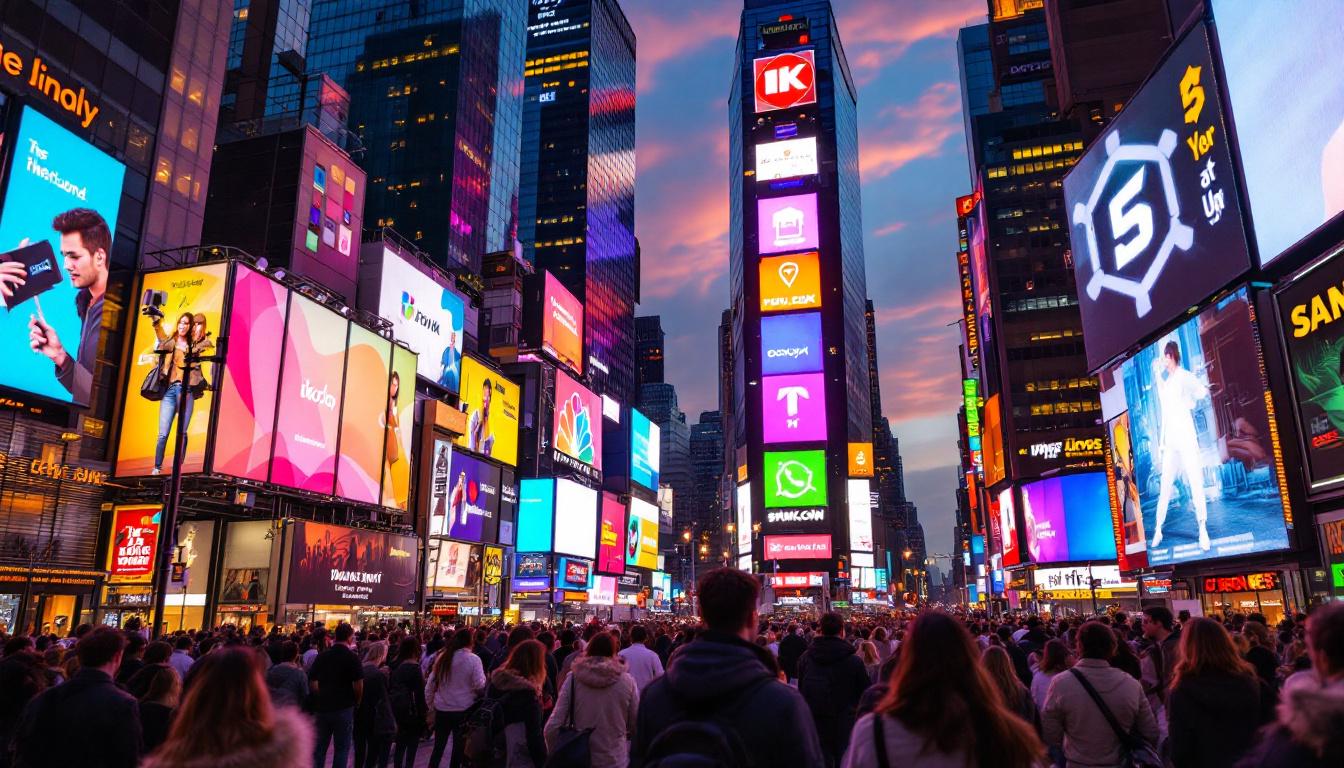
Advertising and Signage
In the advertising industry, SMD LEDs are widely used for digital billboards and signage. Their brightness and clarity ensure that advertisements are visible even in bright daylight. Furthermore, the ability to change content quickly and easily makes SMD LED displays a dynamic advertising medium. This flexibility allows businesses to tailor their messages to different audiences and times of day, optimizing engagement and effectiveness. Additionally, the integration of smart technology with SMD LED displays has paved the way for interactive advertising, where consumers can engage with content through their smartphones, enhancing the overall marketing strategy.
Automotive Lighting
Automotive manufacturers have also embraced SMD LED technology for various lighting applications, including headlights, taillights, and interior lighting. The high brightness and energy efficiency of SMD LEDs enhance visibility and safety on the road, while their compact size allows for innovative design solutions. In recent years, the trend has shifted towards adaptive lighting systems that utilize SMD LEDs, which can adjust the beam pattern based on driving conditions, improving nighttime visibility. Moreover, the longevity of SMD LEDs reduces the need for frequent replacements, which is a significant advantage for both manufacturers and consumers, contributing to lower maintenance costs and a more sustainable automotive industry.
Architectural Lighting
Beyond consumer electronics and automotive applications, SMD LEDs are making significant strides in architectural lighting. Their ability to produce a wide spectrum of colors and their compact form factor allow for creative and intricate lighting designs in both commercial and residential spaces. From illuminating facades of skyscrapers to accentuating art installations, SMD LEDs provide architects and designers with the flexibility to create stunning visual effects. Additionally, the energy efficiency of SMD LEDs contributes to sustainable building practices, as they consume less power and have a longer lifespan compared to traditional lighting solutions. This has led to a growing trend in smart lighting systems that can be controlled remotely, allowing users to adjust brightness and color to suit different moods and occasions.
How SMD LEDs Work
To fully appreciate the capabilities of SMD LEDs, it is essential to understand how they function. The operation of an SMD LED involves several key components and processes.
The Semiconductor Process
At the heart of every SMD LED is a semiconductor chip. When an electric current is applied to the chip, electrons are excited and move across the semiconductor material. As these electrons return to their original state, they release energy in the form of photons, which is the light that we see. The color of the light emitted depends on the materials used in the semiconductor chip.
Heat Management
Heat management is crucial for the performance and longevity of SMD LEDs. While they are more efficient than traditional lighting solutions, SMD LEDs still generate heat during operation. Proper heat dissipation mechanisms, such as heat sinks or thermal pads, are often incorporated into the design to prevent overheating and ensure optimal performance.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their many advantages, SMD LEDs also come with certain challenges and considerations that manufacturers and consumers should be aware of.
Initial Cost
While the long-term savings associated with energy efficiency and longevity are significant, the initial cost of SMD LED technology can be higher than traditional lighting options. This upfront investment can be a barrier for some consumers and businesses, although prices have been steadily decreasing as technology advances.
Color Consistency
Another challenge with SMD LEDs is achieving color consistency across different batches. Variations in manufacturing processes can lead to differences in color output, which can be problematic for applications requiring uniformity, such as in display screens. Quality control measures are essential to mitigate these issues.
The Future of SMD LED Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the future of SMD LEDs looks promising. Innovations in materials, design, and manufacturing processes are paving the way for even more efficient and versatile lighting solutions.
Advancements in Efficiency
Research and development in the field of semiconductor materials are expected to yield SMD LEDs that are even more energy-efficient. New materials may also allow for greater color accuracy and brightness, enhancing their appeal in various applications.
Integration with Smart Technology
With the rise of smart technology, SMD LEDs are increasingly being integrated into smart home systems. This integration allows users to control lighting remotely, set schedules, and customize lighting scenes, providing enhanced convenience and energy savings.
Conclusion
In summary, SMD LEDs represent a significant advancement in lighting and display technology. Their compact size, energy efficiency, and versatility make them an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to large-scale advertising. While challenges such as initial costs and color consistency exist, ongoing advancements in technology promise to address these issues and further enhance the capabilities of SMD LEDs.
As industries continue to adopt this innovative technology, the future of SMD LEDs appears bright, paving the way for smarter, more efficient lighting solutions that meet the demands of modern society.
Illuminate Your Space with LumenMatrix
As you embrace the future of SMD LED technology, consider LumenMatrix as your partner in innovation. Our extensive range of LED display modules, from Indoor and Outdoor LED Wall Displays to specialized solutions like Vehicle and Sports Displays, are designed to bring your visual communication to life. Experience the transformative power of LED displays with LumenMatrix and let us help you create immersive environments that captivate and engage. Ready to revolutionize your space with unparalleled clarity and impact? Check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today and see the difference cutting-edge technology can make.