In today’s digital age, video displays are an integral part of how we communicate, advertise, and entertain. Among the various display technologies available, LED displays have emerged as a dominant force due to their brightness, durability, and versatility. This article explores the intricacies of LED displays, explaining how they work, their advantages, types, and applications across different industries.
Understanding LED Display Technology
What is an LED Display?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. An LED display is a flat panel display that uses an array of these tiny LEDs to create images, videos, and text. Unlike traditional LCDs that rely on backlighting, LED displays use these diodes as the light source, which allows for greater brightness and contrast. This inherent brightness makes LED displays particularly effective in outdoor settings, where sunlight can wash out the visibility of other types of screens.
The LEDs used in video displays can be red, green, and blue, which combine to produce a full spectrum of colors. By controlling the intensity of each diode, the display can render detailed, vibrant images. This capability makes LED displays ideal for environments where visibility and color accuracy are critical. Additionally, the longevity of LED technology contributes to lower maintenance costs, as these displays can last tens of thousands of hours, significantly outpacing traditional display technologies.
How Do LED Displays Work?
Each pixel on an LED display is made up of three sub-pixels: red, green, and blue LEDs. These sub-pixels are individually controlled to vary their brightness, mixing colors to produce the desired output. The process is similar to how pixels work on other digital screens but with the advantage of emitting their own light. This self-illuminating property not only enhances color saturation but also allows for thinner display designs, making them more versatile for various applications, from smartphones to large-scale advertising boards.
LED displays are typically controlled by a driver circuit that manages the current and voltage supplied to each diode. Advanced control systems allow for high refresh rates and precise color calibration, ensuring smooth motion and accurate color reproduction. This technology is scalable, from small indoor screens to massive outdoor billboards. Furthermore, many modern LED displays incorporate smart technology, enabling features such as remote management, real-time content updates, and integration with other digital systems, which broadens their functionality and enhances user engagement.
Types of LED Displays
Indoor vs. Outdoor LED Displays
LED displays are broadly categorized into indoor and outdoor types, each designed to meet specific environmental and performance requirements.
Indoor LED Displays: These are used in environments such as conference rooms, retail stores, and stadiums. They have a higher pixel density (smaller pixel pitch), which means the LEDs are packed closer together. This results in sharper images when viewed from shorter distances. Indoor displays typically have brightness levels ranging from 800 to 1,500 nits, sufficient for controlled lighting conditions.
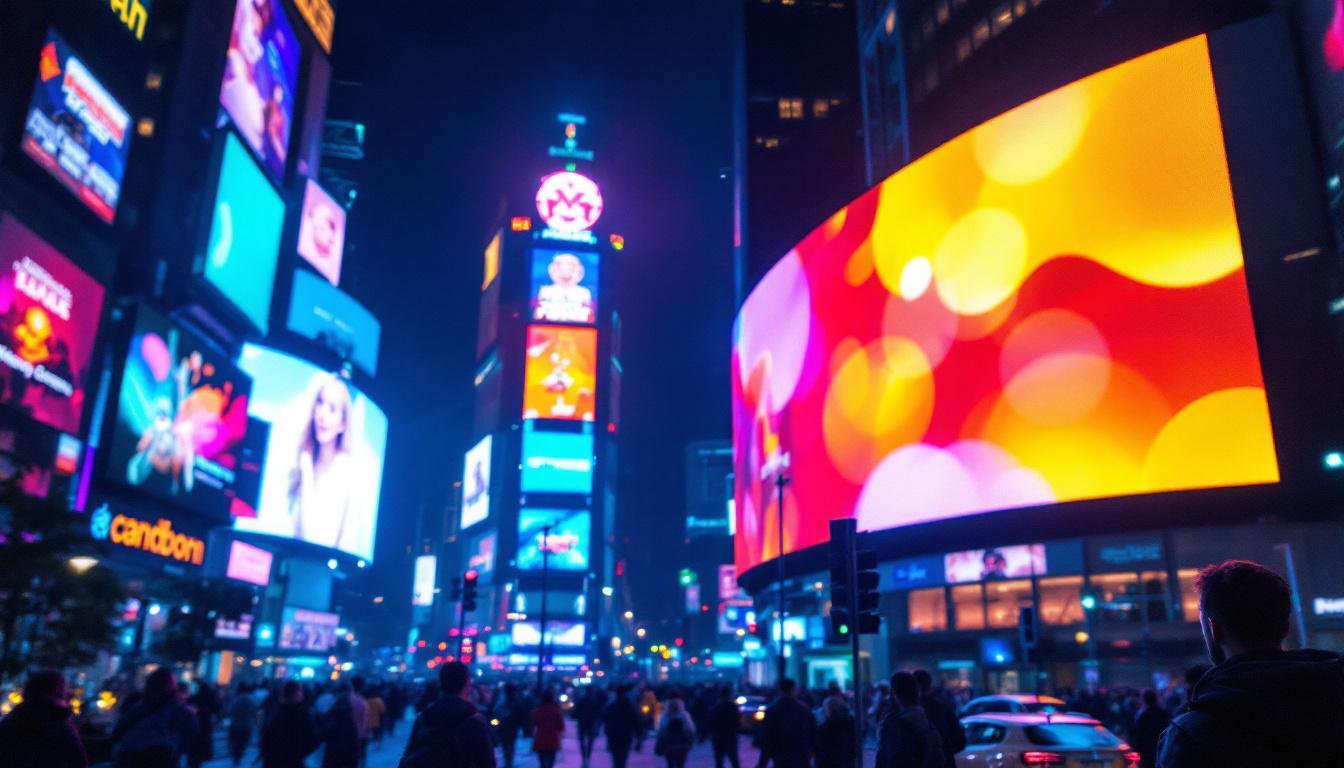
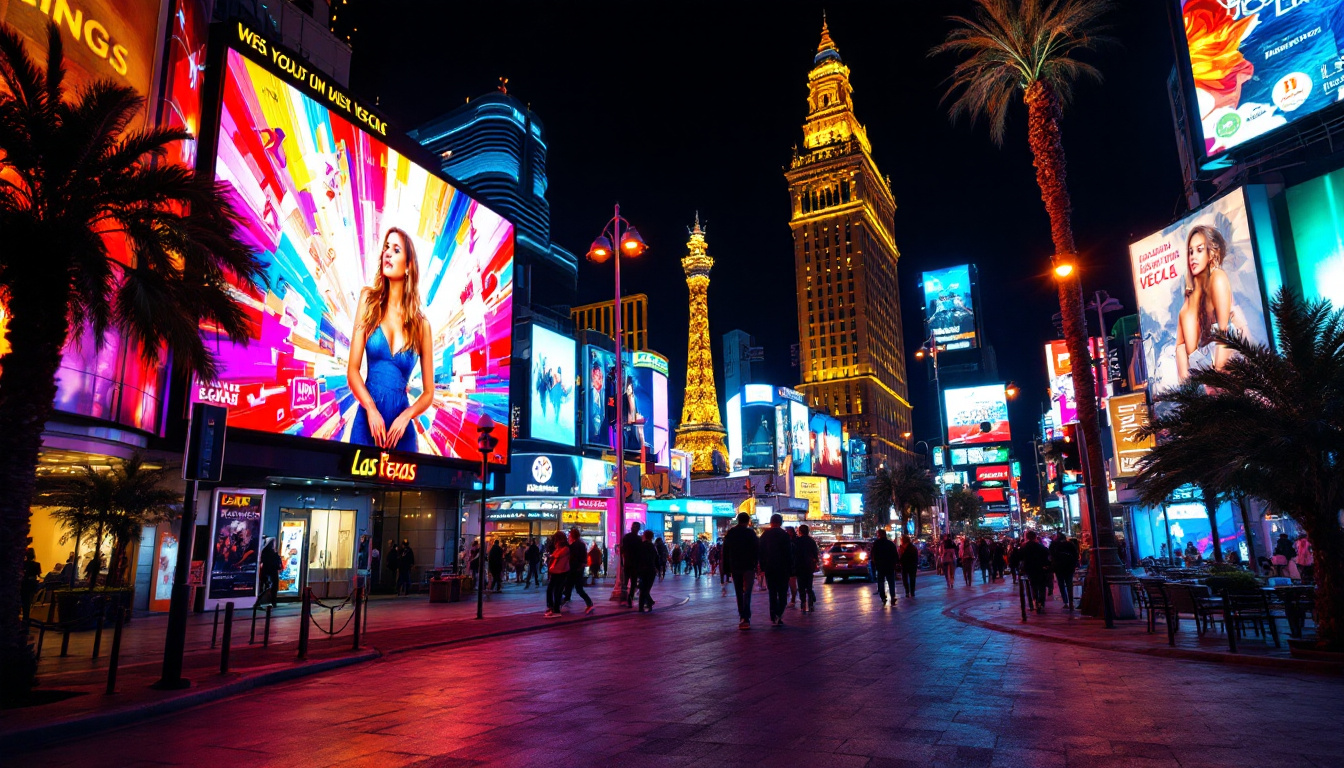
Outdoor LED Displays: Designed to withstand harsh weather conditions, these displays are brighter, often exceeding 5,000 nits, to remain visible under direct sunlight. They also feature protective coatings and robust enclosures to resist moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations. Due to viewing distances being greater outdoors, outdoor LED displays usually have a larger pixel pitch.
Direct View LED vs. LED Backlit LCD
It’s important to distinguish between direct view LED displays and LED-backlit LCD screens. Direct view LED displays use LEDs as the primary light source and image generator, while LED-backlit LCDs use LEDs only to illuminate an LCD panel.
Direct view LED displays offer superior contrast ratios, wider viewing angles, and better color saturation. They are ideal for large-scale applications like stadium screens and digital billboards. LED-backlit LCDs, on the other hand, are common in consumer electronics such as televisions and monitors, where cost and resolution are balanced for everyday use.
Advantages of LED Displays
Brightness and Visibility
One of the most significant advantages of LED displays is their exceptional brightness. With the ability to produce thousands of nits, LED screens remain clearly visible even in bright daylight. This makes them the preferred choice for outdoor advertising, traffic signs, and public information displays.
Moreover, LED technology allows for dynamic brightness adjustment, optimizing visibility depending on ambient light conditions. This adaptability not only enhances viewer experience but also conserves energy by reducing brightness when full power is unnecessary.
Energy Efficiency and Longevity
Compared to traditional display technologies such as plasma or incandescent lighting, LEDs consume significantly less power. This energy efficiency translates into lower operating costs, especially for large installations that run continuously.
LEDs also have a longer lifespan, often exceeding 100,000 hours of use before brightness diminishes noticeably. This durability reduces maintenance costs and downtime, making LED displays a cost-effective solution over the long term.
Flexibility and Customization
LED displays offer remarkable design flexibility. They can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, including curved, transparent, or flexible panels. This versatility enables creative applications in architecture, retail, and entertainment.
Additionally, modular LED panels allow for easy scaling and maintenance. Damaged sections can be replaced without dismantling the entire display, and content can be customized dynamically to suit different audiences or events.
Applications of LED Displays
Advertising and Digital Signage
Advertising is perhaps the most visible application of LED display technology. Digital billboards powered by LEDs have transformed the outdoor advertising landscape, offering vibrant, eye-catching visuals that can be updated in real time. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global digital signage market is expected to reach $31.71 billion by 2028, with LED displays playing a pivotal role in this growth.
Retailers use LED displays to attract customers and promote products, while transportation hubs employ them for real-time information and wayfinding. The ability to deliver dynamic content tailored to time of day, weather, or audience demographics enhances engagement and effectiveness.
Sports and Entertainment Venues
Stadiums and arenas rely heavily on LED displays to enhance the spectator experience. Large-scale video walls provide instant replays, live feeds, and interactive content. The high brightness and wide viewing angles ensure visibility from any seat, even under challenging lighting conditions.
Concerts and theaters incorporate LED screens for immersive visual effects, complementing performances with synchronized lighting and video. The lightweight and modular nature of LED panels make them ideal for temporary installations and touring events.
Corporate and Educational Settings
In corporate environments, LED displays are used for presentations, video conferencing, and digital dashboards. Their clarity and brightness improve communication and collaboration, especially in large meeting rooms or auditoriums.
Educational institutions utilize LED displays for interactive learning, digital signage, and event broadcasting. The technology supports multimedia content delivery, making lessons more engaging and accessible.
Key Considerations When Choosing an LED Display
Pixel Pitch and Resolution
Pixel pitch refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent pixels and is a crucial factor in determining image clarity. A smaller pixel pitch means higher resolution and sharper images, which is essential for close viewing distances.
For indoor applications where viewers are close to the screen, pixel pitches can be as small as 0.9mm. Outdoor displays typically have larger pixel pitches, ranging from 4mm to 20mm or more, optimized for visibility at greater distances.
Brightness and Contrast Ratio
Brightness is measured in nits, and selecting the appropriate level depends on the installation environment. Outdoor displays require higher brightness to combat sunlight, while indoor displays benefit from higher contrast ratios for better image depth.
Contrast ratio, the difference between the darkest black and the brightest white, affects image quality. LED displays generally offer superior contrast compared to other technologies, enhancing the viewing experience.
Durability and Weather Resistance
For outdoor installations, durability is paramount. LED displays must be rated for ingress protection (IP rating) to ensure resistance to water, dust, and other environmental factors. IP65 or higher is common for outdoor screens, guaranteeing protection against rain and debris.
Temperature tolerance is also critical, as LED displays may be exposed to extreme heat or cold. Quality LED modules incorporate thermal management systems to maintain performance and longevity under varying conditions.
The Future of LED Displays
Technological Innovations
Advancements in LED technology continue to push the boundaries of what video displays can achieve. MicroLED, a next-generation display technology, uses microscopic LEDs to create even higher resolution and brightness with lower power consumption. Although still emerging, MicroLED promises to revolutionize displays in smartphones, TVs, and large-scale video walls.
Flexible and transparent LED displays are also gaining traction, enabling new design possibilities in architecture and automotive industries. These innovations will expand the use cases and integration of LED displays in everyday life.
Integration with Smart Technologies
LED displays are increasingly integrated with IoT (Internet of Things) and AI-driven content management systems. This integration allows for real-time data-driven content updates, personalized advertising, and interactive user experiences.
For example, smart city initiatives employ LED displays to provide dynamic public information, traffic updates, and emergency alerts, enhancing urban living and safety.
Conclusion
LED displays have transformed the landscape of video display technology through their superior brightness, energy efficiency, and versatility. From advertising and entertainment to corporate and educational applications, they offer unparalleled visual impact and adaptability.
As technology advances, LED displays will continue to evolve, offering higher resolutions, innovative form factors, and smarter integration. Understanding the fundamentals of LED technology and its practical considerations empowers businesses and organizations to make informed decisions, maximizing the benefits of this powerful display medium.
Discover LumenMatrix’s Innovative LED Solutions
Ready to elevate your visual communication with cutting-edge LED technology? Explore LumenMatrix’s comprehensive range of LED display modules, designed to captivate and engage your audience. From vibrant Indoor and Outdoor LED Wall Displays to dynamic Vehicle and Sports LED Displays, LumenMatrix offers tailored solutions that bring your brand to life. Experience the future of digital signage with our All-in-One, Custom, and Transparent LED Displays. Check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today and transform your message into an unforgettable visual experience.