In today’s fast-paced digital world, LED displays have become an integral part of advertising, entertainment, and information dissemination. From vibrant billboards in Times Square to dynamic scoreboards in stadiums, LED technology powers some of the most eye-catching visuals we encounter daily. But what exactly is an LED display, and how does the concept of a “pixel cart” fit into this technology? This article delves deep into the world of LED displays, explaining their structure, functionality, and the role of pixels and pixel carts in creating stunning visual experiences.
Understanding LED Displays: The Basics
What is an LED Display?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. An LED display is a flat panel that uses an array of LEDs as pixels to create images, videos, and animations. These displays are widely used because of their brightness, energy efficiency, and long lifespan compared to traditional display technologies like LCD or plasma.
LED displays come in various forms, including indoor and outdoor screens, flexible panels, and transparent displays. They are used for advertising, digital signage, stage backdrops, traffic signals, and even wearable technology. Their versatility and scalability make them suitable for small handheld devices as well as massive outdoor billboards. In fact, the outdoor LED market has seen explosive growth in recent years, with businesses leveraging these displays to capture consumer attention in high-traffic areas. The vibrant colors and high visibility of LED displays ensure that advertisements stand out, even in bright sunlight or adverse weather conditions.
The Anatomy of an LED Display
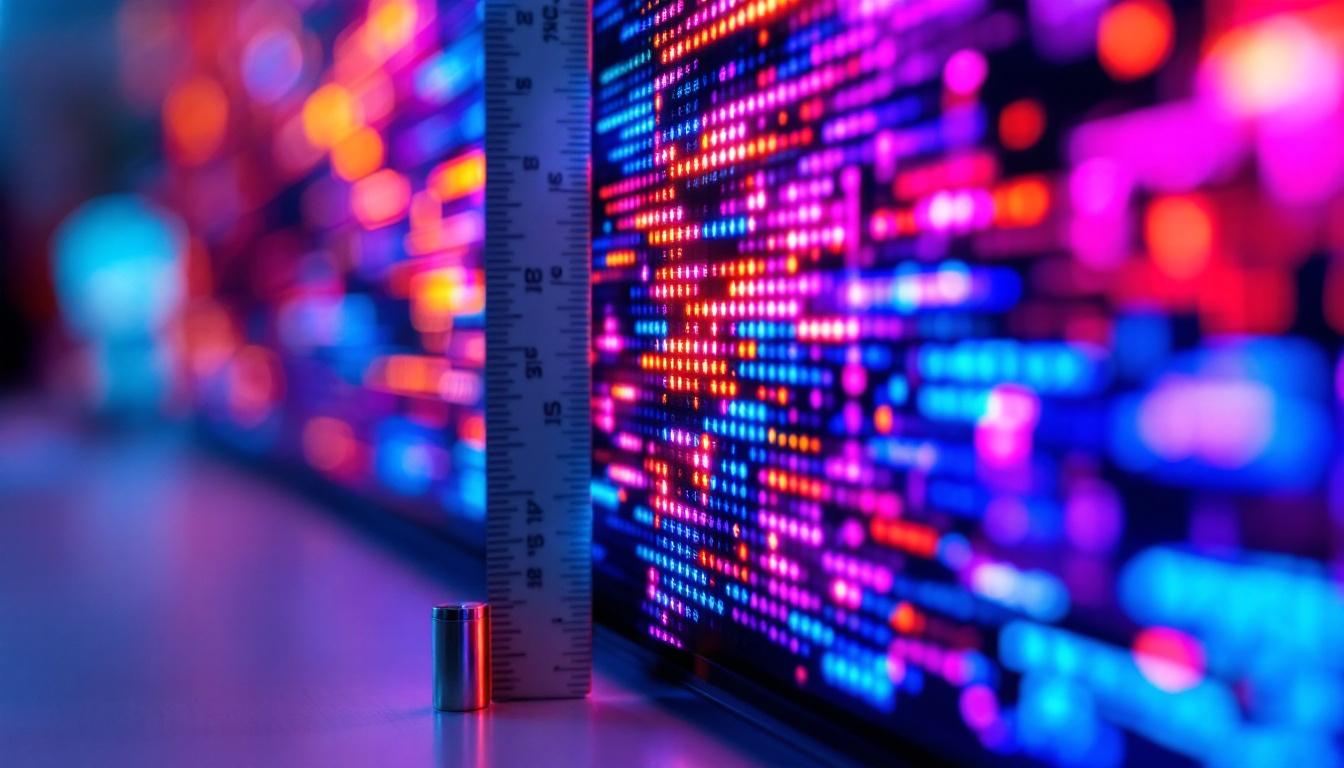
At its core, an LED display consists of thousands to millions of tiny LEDs arranged in a grid pattern. Each LED acts as a single pixel or part of a pixel, which can emit different colors by combining red, green, and blue (RGB) LEDs. When these pixels light up in various intensities, they create the images and videos we see on the screen.
Each pixel is controlled individually through a complex system of drivers and controllers that regulate the color and brightness. The resolution of an LED display depends on the number of pixels per unit area, commonly referred to as pixel pitch, which is the distance between the centers of two adjacent pixels. A smaller pixel pitch means higher resolution and sharper images, especially important for close viewing distances. Moreover, advancements in technology have led to the development of microLED and miniLED displays, which offer even greater pixel density and improved color accuracy. These innovations are paving the way for future applications in virtual reality and augmented reality, where immersive experiences demand the highest quality visuals.
In addition to resolution, the refresh rate of an LED display plays a crucial role in delivering smooth motion and reducing flicker, particularly in video content. A higher refresh rate ensures that fast-moving images appear fluid and clear, making LED displays ideal for sports events, concerts, and gaming. Furthermore, the durability of LED technology means that these displays can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them a popular choice for outdoor installations that require resilience against rain, wind, and temperature fluctuations. As the demand for high-performance displays continues to rise, manufacturers are constantly innovating to enhance the capabilities and applications of LED technology.
What is a Pixel Cart in LED Displays?
Defining the Pixel Cart
The term “pixel cart” is less commonly known outside of specialized LED display manufacturing and installation circles but is crucial for understanding how LED displays are assembled and maintained. A pixel cart refers to a modular unit or frame that holds a group of pixels (LED modules) together. It serves as a building block for larger LED screens, allowing for easier transportation, installation, and repair.
Think of a pixel cart as a “cart” or carrier for pixels, where each cart contains a matrix of LEDs arranged to form a section of the overall display. These carts can be snapped together like building blocks to create a seamless, large-format screen. This modular approach enhances flexibility, enabling displays to be customized in size and shape according to specific requirements.
Why Pixel Carts Matter
Pixel carts streamline the manufacturing and maintenance processes of LED displays. Instead of handling millions of individual LEDs, technicians work with manageable modules. This modularity reduces downtime during repairs because faulty pixel carts can be swapped out quickly without dismantling the entire display.
Moreover, pixel carts facilitate scalability. Event organizers or advertisers can rent or purchase pixel carts to assemble temporary or permanent displays tailored to their venue size. This adaptability is particularly valuable for touring concerts, trade shows, and outdoor advertising where display dimensions often vary.
How LED Pixels Work: From Light to Image
The RGB Pixel Model
Each pixel in an LED display is typically composed of three sub-pixels: red, green, and blue LEDs. By varying the intensity of each sub-pixel, the display can produce a broad spectrum of colors through additive color mixing. For example, combining red and green light creates yellow, while all three at full intensity produce white.
This RGB model is fundamental to all color LED displays. The precision with which these sub-pixels are controlled determines the color accuracy and vibrancy of the final image. Modern LED displays can render millions of colors, making them suitable for high-definition video playback and detailed graphics.
Pixel Pitch and Viewing Distance
Pixel pitch plays a critical role in image clarity. A smaller pixel pitch means pixels are closer together, resulting in higher resolution and finer detail. For indoor displays viewed from a few feet away, pixel pitches as small as 1.2mm are common. Outdoor displays, viewed from greater distances, often have larger pixel pitches, such as 10mm or more, balancing cost and visibility.
Choosing the right pixel pitch is essential to avoid pixelation or blurriness. For example, a billboard on a highway might have a pixel pitch of 16mm because viewers are far away, whereas a retail store’s indoor display might use a 2.5mm pitch for crisp images up close.
Applications of Pixel Carts and LED Displays
Advertising and Digital Signage
One of the most visible uses of LED displays is in advertising. Brands leverage large LED billboards and digital signage to capture consumer attention with dynamic content. Pixel carts enable these displays to be customized in size and shape to fit unique architectural spaces, such as curved building facades or irregularly shaped storefronts.
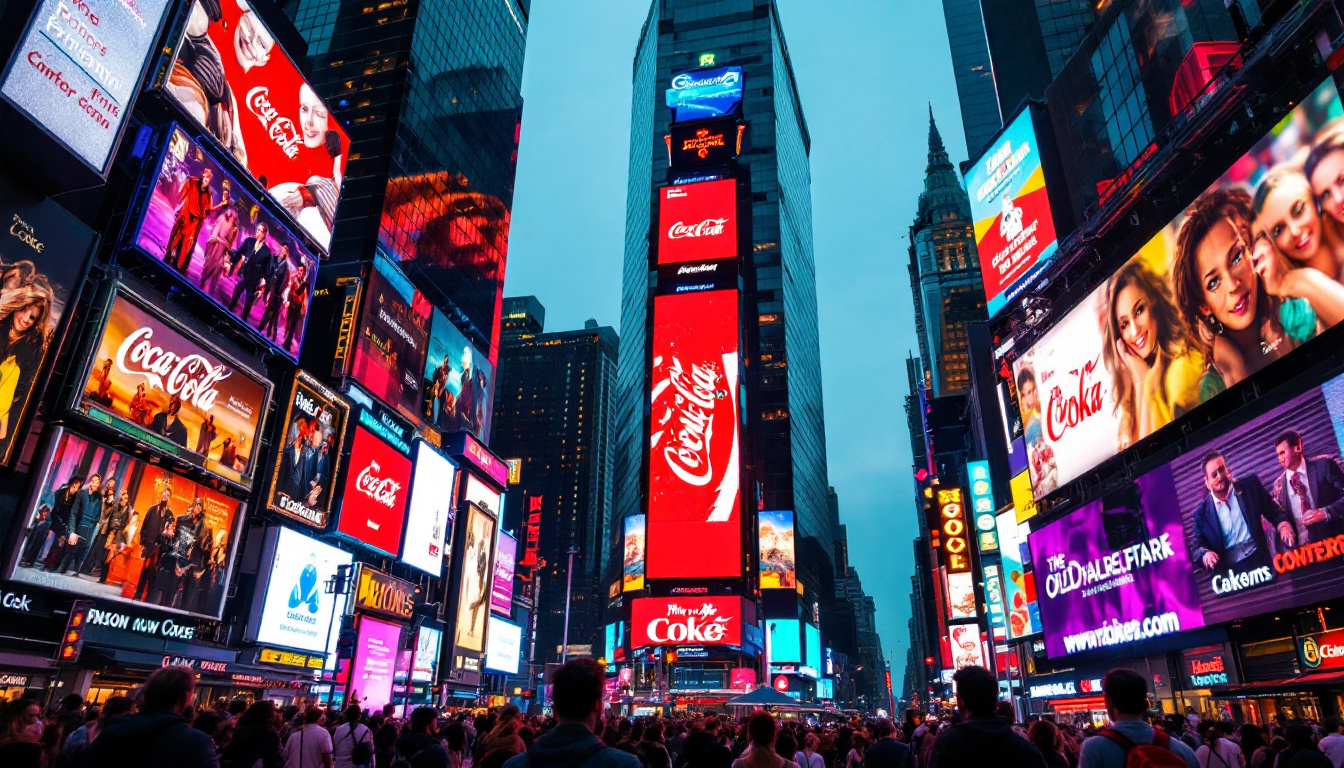
For example, the famous LED screens in New York’s Times Square use modular LED panels that can be considered pixel carts, allowing for easy maintenance and upgrades. This modularity ensures that advertisers can display high-resolution, vibrant content that stands out in a crowded urban environment.
Entertainment and Events
Concerts, festivals, and sporting events frequently use massive LED screens to enhance the audience experience. Pixel carts make it possible to assemble large, high-resolution displays quickly and dismantle them just as fast after the event. This flexibility is crucial for touring productions that require reliable, transportable visual solutions.
For instance, the LED backdrop for a major music festival might consist of dozens of pixel carts, each containing thousands of LEDs, combined to create a seamless video wall that complements the live performance.
Architectural and Ambient Displays
Beyond traditional screens, LED technology is increasingly integrated into architectural elements, creating ambient lighting and dynamic façades. Pixel carts facilitate the integration of LED modules into building designs, allowing architects to incorporate programmable light patterns and images into walls, ceilings, and even floors.
Such installations not only enhance aesthetics but can also provide functional lighting or interactive experiences. For example, a hotel lobby might feature a large LED wall composed of pixel carts that display calming visuals or promotional content, adapting throughout the day.
Technological Advances in LED Displays
Mini-LED and Micro-LED Innovations
Recent advancements in LED technology have introduced mini-LED and micro-LED displays, which use significantly smaller LEDs to achieve even higher resolutions and improved color accuracy. These technologies push the boundaries of pixel density, enabling displays with pixel pitches below 1mm.
Micro-LEDs, in particular, offer superior brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LEDs and OLEDs. While still emerging in commercial markets, micro-LED technology is expected to revolutionize display industries, including smartphones, TVs, and large-scale LED walls.
Improved Control Systems and Software
Modern LED displays rely on sophisticated control systems that manage pixel brightness, color calibration, and synchronization. Software advancements allow for real-time content updates, remote monitoring, and automated diagnostics, enhancing operational efficiency.
Pixel carts integrate seamlessly with these control systems, enabling modular troubleshooting and precise calibration. This integration ensures that even large, complex displays maintain uniformity and performance over time.
Choosing the Right LED Display and Pixel Cart Setup
Factors to Consider
Selecting the appropriate LED display involves evaluating several factors, including viewing distance, ambient lighting conditions, resolution requirements, and budget. Understanding pixel pitch and the modularity offered by pixel carts helps in designing a display that meets specific needs.
For outdoor advertising, durability and weather resistance are critical, while indoor displays prioritize color accuracy and viewing angles. Additionally, the ease of installation and maintenance, facilitated by pixel carts, can influence the total cost of ownership.
Working with Professionals
Given the technical complexity of LED displays, collaborating with experienced manufacturers and installers is essential. Professionals can recommend the optimal pixel pitch, pixel cart configuration, and control systems tailored to the application.
They also ensure compliance with safety standards and provide ongoing support, maximizing the lifespan and effectiveness of the LED display investment.
Conclusion: The Future of Pixel Carts and LED Displays
LED displays continue to transform how information and entertainment are delivered in public and private spaces. The concept of the pixel cart exemplifies the modular, scalable nature of modern LED technology, enabling flexible, high-quality visual solutions across industries.
As LED technology advances with innovations like micro-LEDs and smarter control systems, pixel carts will evolve to support even more intricate and immersive displays. For businesses and event organizers, understanding these components is key to leveraging LED displays for maximum impact and engagement.
Whether for advertising, entertainment, or architectural design, LED displays powered by pixel carts represent a dynamic and versatile medium that will shape visual communication for years to come.
Discover the Future of Visuals with LumenMatrix
Ready to elevate your visual experience and captivate your audience like never before? LumenMatrix is at the forefront of LED display innovation, offering a comprehensive range of solutions tailored to your unique needs. From Indoor and Outdoor LED Wall Displays to specialized options like Vehicle, Sports, and Floor LED Displays, our products are designed to make your brand shine. Embrace the future of visual communication with our Custom, All-in-One, and Transparent LED Displays. Check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today and transform your space into a dynamic canvas of light and color.