In the world of digital visuals, LED displays have revolutionized how information and entertainment are presented. From towering billboards in Times Square to the vibrant screens in smartphones and televisions, LED technology plays a crucial role in delivering bright, crisp, and dynamic images. But what exactly goes into creating these dazzling displays? This article delves into the intricacies of LED displays, explaining the concept of pixels, how LED technology works, and why it remains the preferred choice for a wide range of applications.
Understanding Pixels: The Building Blocks of LED Displays
At the heart of any digital display lies the pixel — the smallest unit of a digital image. The term “pixel” is a contraction of “picture element,” and it represents a single point of light or color on a screen. When thousands or millions of these pixels are combined, they form the images and videos we see.
In LED displays, each pixel is typically composed of tiny light-emitting diodes that can produce red, green, and blue light. By varying the intensity of these three colors, a pixel can display a vast spectrum of colors. This RGB (red, green, blue) model is fundamental to digital color representation.
Pixel Density and Resolution
One of the most important factors in display quality is pixel density, often measured in pixels per inch (PPI). Higher pixel density means more pixels are packed into a given area, resulting in sharper and more detailed images. For example, a smartphone screen with 400 PPI will appear much crisper than a billboard with 50 PPI, simply because the viewing distance and use case differ significantly.
Resolution refers to the total number of pixels in a display, typically expressed as width × height (e.g., 1920×1080). Higher resolutions mean more pixels, which generally translates to clearer images. However, the practical impact of resolution depends on screen size and viewing distance. For instance, while a 4K resolution (3840×2160) provides an impressive level of detail on a large television screen, the difference may be less noticeable on a smaller device held closer to the eyes, where the pixel density compensates for the resolution.
Moreover, advancements in display technology continue to push the boundaries of pixel density and resolution. Innovations such as Retina displays and 8K resolution screens are becoming increasingly common, offering users an unparalleled viewing experience. These technologies utilize advanced algorithms and pixel arrangements to enhance image clarity, making it difficult for the naked eye to discern individual pixels even at close distances. This leap in technology not only elevates the quality of visual content but also impacts various industries, from gaming and film to medical imaging and graphic design, where precision and detail are paramount.
How LED Displays Work: Technology Behind the Glow
LED displays function by controlling the brightness and color of individual light-emitting diodes arranged in a grid. Each diode emits light when an electric current passes through it, and by adjusting the current, the display can control the intensity of each color channel within a pixel.
Types of LED Displays
There are several types of LED displays, each suited for different applications:
- Direct View LED (DVLED): These displays use LEDs as the actual pixels, making them extremely bright and suitable for large outdoor screens and stadium displays.
- LED-backlit LCD: This common technology uses LEDs as a backlight source behind an LCD panel. It offers excellent color accuracy and contrast for televisions, monitors, and smartphones.
- MicroLED: An emerging technology that uses microscopic LEDs to create displays with superior brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency compared to OLED and LCD.
Color and Brightness Control
Each pixel in an LED display contains subpixels for red, green, and blue light. By adjusting the voltage to each subpixel, the display can produce millions of color combinations. This precise control enables the vibrant and lifelike images seen on modern screens.
Brightness is another critical aspect. Outdoor LED displays, for instance, must be extremely bright to remain visible under direct sunlight, often exceeding 5,000 nits. In contrast, indoor displays typically operate around 300 to 500 nits, balancing visibility with eye comfort.
Moreover, the technology behind LED displays has evolved significantly over the years, with advancements in color calibration and dynamic range. High Dynamic Range (HDR) technology, for example, enhances the contrast between the darkest and brightest parts of an image, allowing for a more immersive viewing experience. This feature is particularly beneficial in environments where lighting conditions can vary dramatically, ensuring that the display remains effective regardless of external factors.
Additionally, the lifespan and durability of LED displays are noteworthy attributes. Unlike traditional display technologies, LEDs are known for their longevity, often lasting over 50,000 hours of use. This durability makes them a cost-effective solution for both commercial and residential applications, as they require less frequent replacements and maintenance. The robust nature of LED technology also means they can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them ideal for outdoor installations where exposure to the elements is a concern.
Applications of LED Displays: From Advertising to Entertainment
LED displays are everywhere, serving a wide variety of purposes across industries. Their versatility, brightness, and durability make them ideal for many environments.
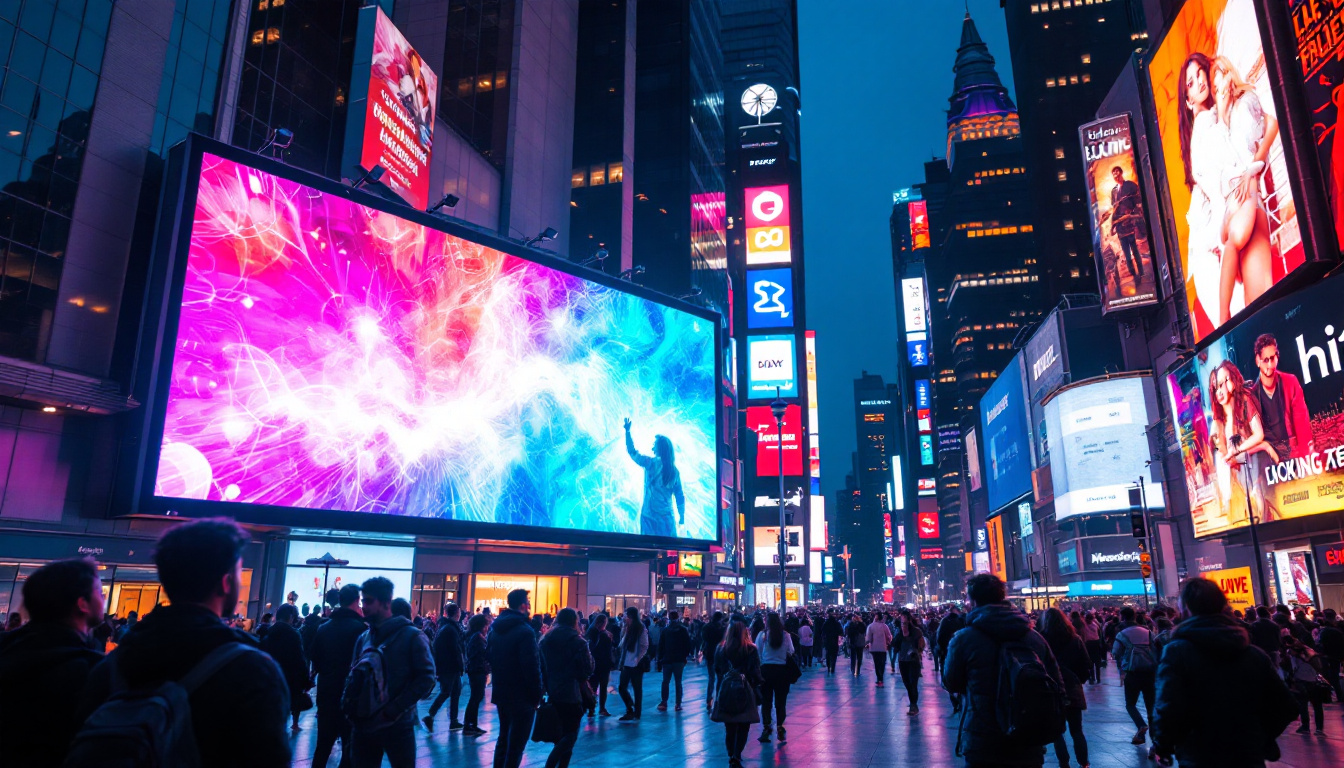
Outdoor Advertising and Digital Billboards
Digital billboards are among the most visible applications of LED displays. Their ability to display dynamic content — including video, animations, and real-time updates — makes them far more engaging than traditional static signs. According to industry reports, the global digital billboard market is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 11% through 2027, driven by urbanization and increased advertising spending.
These displays often use direct view LED technology to ensure visibility in all weather conditions and lighting environments. Pixel pitch — the distance between individual LEDs — is a crucial factor here. Larger pixel pitches (e.g., 10mm or more) are acceptable for billboards viewed from hundreds of feet away, while smaller pitches are used for closer viewing distances.
Consumer Electronics: TVs, Smartphones, and Wearables
In consumer electronics, LED technology has transformed display quality and energy efficiency. LED-backlit LCDs dominate the television market, offering high-definition visuals with excellent color reproduction. Meanwhile, OLED and MicroLED technologies are pushing boundaries by providing even deeper blacks and higher contrast ratios.
Smartphones benefit from high pixel density LED displays, often exceeding 400 PPI, delivering sharp text and vivid images on relatively small screens. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches, use small LED displays optimized for low power consumption and readability in various lighting conditions.
Events, Stadiums, and Public Spaces
Large-scale LED displays are common in sports arenas, concert venues, and public spaces. Their ability to display live video feeds, advertisements, and interactive content enhances the spectator experience. For example, the LED ribbon boards circling basketball arenas provide real-time scores and sponsor messages, seamlessly integrating technology with entertainment.
Advantages and Challenges of LED Displays
LED displays offer numerous benefits, but they also come with certain challenges that manufacturers and users must consider.
Advantages
- Brightness and Visibility: LEDs provide superior brightness, making displays visible in bright daylight and large venues.
- Energy Efficiency: Compared to older technologies like CCFL backlighting, LEDs consume less power, which is critical for battery-powered devices and large installations.
- Longevity and Durability: LEDs have a long lifespan, often exceeding 50,000 hours, and are resistant to shock and vibration.
- Color Accuracy and Contrast: LED displays can produce vivid colors and deep blacks, enhancing image quality.
Challenges
- Cost: High-quality LED displays, especially those with fine pixel pitch or MicroLED technology, can be expensive to produce and install.
- Heat Management: LEDs generate heat, which must be managed to maintain performance and longevity.
- Pixel Pitch Limitations: For extremely close viewing distances, LED displays require very fine pixel pitches, which can increase complexity and cost.
- Environmental Impact: While energy efficient, the manufacturing and disposal of LED components involve environmental considerations.
The Future of LED Displays: Trends to Watch
As display technology continues to evolve, LED displays are at the forefront of innovation. Several trends promise to shape the future landscape of digital visuals.
MicroLED and MiniLED Technologies
MicroLED technology is gaining momentum due to its potential to combine the best features of OLED and traditional LED displays. MicroLEDs offer exceptional brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency without the burn-in issues associated with OLED. Although still costly, advancements in manufacturing are expected to make MicroLED more accessible in the coming years.
MiniLED, which uses smaller LEDs for backlighting in LCD panels, is already making waves in high-end monitors and televisions. It allows for improved local dimming and higher contrast ratios, enhancing picture quality significantly.
Flexible and Transparent LED Displays
Innovation is also driving the development of flexible and transparent LED displays. These technologies open new possibilities for design and application, including wearable devices, automotive dashboards, and augmented reality interfaces. Transparent LED displays can be integrated into windows or glass surfaces, blending digital content with the physical environment.
Integration with AI and IoT
LED displays are increasingly integrated with artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) to deliver personalized and interactive experiences. For example, digital signage can adapt content based on audience demographics or environmental conditions, enhancing engagement and effectiveness.
Conclusion
LED displays have transformed the way visual information is presented across industries, offering unparalleled brightness, color accuracy, and versatility. Understanding the role of pixels, the underlying technology, and the various applications helps appreciate the complexity and innovation behind these ubiquitous screens. As advancements like MicroLED and flexible displays emerge, LED technology is poised to become even more integral to our digital lives, continuing to illuminate the future of visual communication.
Illuminate Your World with LumenMatrix
Ready to elevate your visual experience with the latest in LED technology? LumenMatrix is at the forefront of innovation, offering a diverse range of LED display solutions tailored to your needs. From Indoor and Outdoor LED Wall Displays to dynamic Vehicle and Sports Displays, our products are designed to captivate and engage. Discover the power of our Custom, All-in-One, and Transparent LED Displays, and see how we can transform your space with clarity and impact. Check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions and join the revolution in visual communication.