In today’s rapidly evolving world of television technology, understanding the differences between LED and LCD televisions is essential for making an informed purchase. Both LED and LCD TVs are prevalent in the market, often causing confusion among buyers due to overlapping terminology and similar appearances. This article delves deep into the technology behind these displays, clarifies common misconceptions, and highlights the key differences that impact picture quality, energy efficiency, and overall user experience.
Understanding the Basics: What is LCD Technology?
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display, a technology that has been the backbone of flat-panel TVs for decades. At its core, an LCD TV uses liquid crystals sandwiched between two layers of glass or plastic. These crystals don’t emit light themselves but manipulate light passing through them to create images.
The liquid crystals align in response to electrical currents, controlling the amount of light that passes through each pixel. This process allows the TV to display images by blocking or allowing light in specific areas, producing the colors and shapes seen on the screen.
However, since liquid crystals don’t generate light, LCD TVs require a separate light source, known as a backlight, to illuminate the screen. This is where the distinction between traditional LCD TVs and LED TVs begins to emerge.
The Role of the Backlight in LCD TVs
Initially, LCD TVs used Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps (CCFLs) as their backlight. These fluorescent tubes provided uniform lighting across the screen but had several drawbacks, including bulkier design, higher energy consumption, and limited control over brightness and contrast.
CCFL backlights also struggled with color accuracy and black levels, often resulting in washed-out images and less vibrant displays compared to newer technologies.
In response to these limitations, manufacturers began to adopt LED (Light Emitting Diode) technology for backlighting. LED backlights not only offer a slimmer profile, making TVs lighter and more aesthetically pleasing, but they also provide enhanced brightness and improved energy efficiency. With the ability to dim individual LEDs or use local dimming techniques, LED-backlit LCDs can achieve deeper blacks and a wider color gamut, significantly elevating the viewing experience. This shift has led to a proliferation of LED LCD TVs in the market, with many models now incorporating advanced features like HDR (High Dynamic Range) to further enhance picture quality.
Moreover, the introduction of edge-lit and full-array LED configurations has allowed for even greater flexibility in design and performance. Edge-lit LED TVs use LEDs positioned along the edges of the screen, while full-array models have a grid of LEDs behind the screen, providing more uniform lighting and better contrast. This evolution in backlighting technology has not only improved the visual quality of LCD TVs but has also made them more accessible to a wider audience, as prices have become more competitive over time.
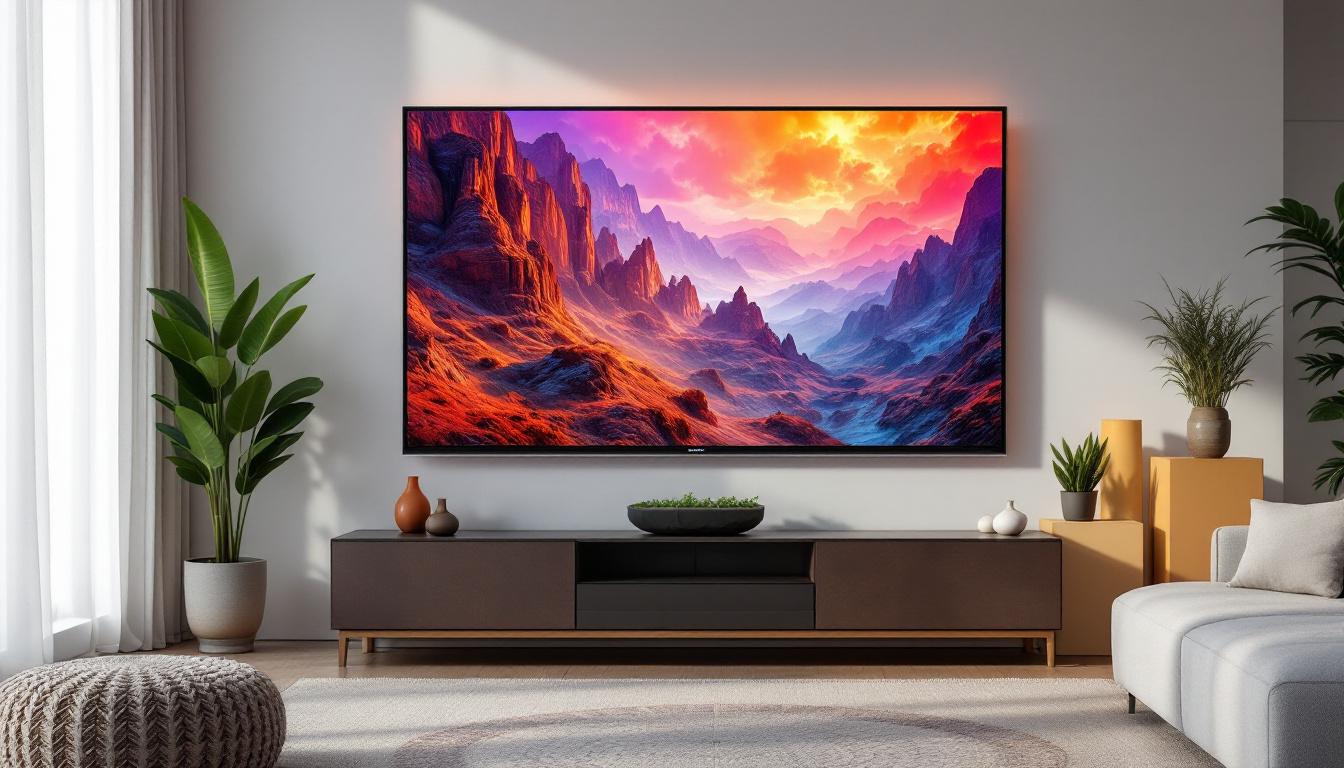
What is LED Television? Clarifying the Misconception
LED TVs are often marketed as a distinct category from LCD TVs, but technically, an LED TV is a type of LCD TV. The primary difference lies in the backlighting technology used.
Instead of CCFLs, LED TVs use Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) as the backlight source. This shift from fluorescent tubes to LEDs brought significant improvements in display quality, energy efficiency, and design flexibility.
Types of LED Backlighting
LED backlighting comes in two main configurations: edge-lit and full-array (also known as direct-lit). Each has its advantages and affects picture quality differently.
- Edge-Lit LED: In this design, LEDs are placed along the edges of the screen. Light is diffused across the display using light guides. Edge-lit LED TVs are typically thinner and lighter, making them popular for sleek designs. However, they may suffer from uneven brightness and less precise contrast control.
- Full-Array LED: This setup involves placing LEDs directly behind the entire screen. Full-array LED TVs often include local dimming zones, allowing parts of the screen to dim independently, enhancing contrast and black levels. This results in deeper blacks and more vibrant images, especially in scenes with high contrast.
Mini-LED and Micro-LED: The Next Evolution
Recent advancements have introduced Mini-LED and Micro-LED backlighting technologies. Mini-LEDs are smaller LEDs that allow for thousands of dimming zones, further improving contrast and brightness control. Micro-LEDs, on the other hand, are self-emissive like OLEDs, meaning each pixel emits its own light, offering exceptional picture quality but currently at a higher cost.
Key Differences Between LED and LCD Televisions
While LED TVs are a subset of LCD TVs, the differences in backlighting technology translate into tangible differences in performance and user experience. Understanding these differences helps consumers choose the right TV for their needs.
Picture Quality and Contrast
LED backlighting, especially with full-array local dimming, provides superior contrast compared to traditional CCFL-backlit LCD TVs. The ability to dim specific zones of the screen results in deeper blacks and more dynamic images.
For example, a scene with a bright moon against a dark sky will appear more realistic on an LED TV with local dimming, as the dark areas can be dimmed without affecting the brightness of the moon.
Color accuracy is also generally better in LED TVs, thanks to improved backlighting and color filters. However, it’s important to note that high-end LCD TVs with CCFL backlights can still offer good picture quality, but they typically lag behind LED models in this regard.
Energy Efficiency
LED backlighting is more energy-efficient than CCFLs, consuming less power and generating less heat. This efficiency translates to lower electricity bills and a smaller environmental footprint.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, LED TVs can use up to 30-40% less energy than comparable CCFL-backlit LCD TVs. This difference becomes significant over the lifespan of the television, especially in households where the TV is used extensively.
Design and Thickness
The smaller size of LEDs allows manufacturers to produce thinner and lighter TVs. Edge-lit LED TVs can be remarkably slim, fitting seamlessly into modern living spaces and mounting flush against walls.
In contrast, CCFL-backlit LCD TVs require more space for the fluorescent tubes, resulting in thicker designs. For consumers prioritizing aesthetics and space-saving, LED TVs offer a clear advantage.
Price Considerations
Generally, LED TVs are priced similarly to LCD TVs because they belong to the same category, but the type of backlighting and additional features affect the cost.
Entry-level edge-lit LED TVs are often competitively priced, while full-array LED TVs with local dimming and advanced features command higher prices. Mini-LED and Micro-LED TVs are positioned as premium products with corresponding price tags.
Additional Factors to Consider When Choosing Between LED and LCD TVs
Viewing Angles
One limitation of both traditional LCD and LED TVs is their narrower viewing angles compared to OLED displays. Colors and contrast can shift when viewed from the side, which may be a concern in wider living rooms or for group viewing.
Some LED TVs incorporate technologies to improve viewing angles, but these improvements vary by model and manufacturer.
Response Time and Gaming Performance
For gamers, response time and input lag are critical factors. LED TVs with faster refresh rates and lower input lag provide smoother gameplay and better responsiveness.
Many modern LED TVs support features like Variable Refresh Rate (VRR) and Auto Low Latency Mode (ALLM), enhancing the gaming experience. While these features are not exclusive to LED TVs, the improved backlighting and panel technologies often found in LED models contribute to better overall performance.
Durability and Lifespan
LED backlights generally have a longer lifespan than CCFLs, with some LED TVs rated for 60,000 to 100,000 hours of use. This durability means that LED TVs can maintain consistent brightness and color quality over many years.
CCFL backlights tend to dim and degrade faster, potentially leading to uneven brightness or color shifts as the TV ages.
Common Misconceptions About LED and LCD TVs
Because marketing often blurs the lines between LED and LCD terminology, several misconceptions persist among consumers.
“LED TVs are completely different from LCD TVs”
As explained earlier, LED TVs are essentially LCD TVs that use LED backlighting instead of CCFLs. The core display technology remains the same, but the backlighting method differs.
“LED TVs are OLED TVs”
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) TVs are a distinct technology where each pixel emits its own light, eliminating the need for backlighting altogether. LED TVs still rely on backlights and liquid crystals to form images. OLEDs generally offer superior contrast and viewing angles but tend to be more expensive.
“More LEDs mean a better TV”
While having more LEDs, especially in full-array local dimming setups, can improve picture quality, it’s not the sole factor defining a TV’s performance. Other elements like panel quality, processing chips, and software optimization play significant roles.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Viewing Needs
Choosing between LED and LCD televisions ultimately comes down to understanding that LED TVs are a type of LCD TV with improved backlighting technology. This advancement results in better picture quality, energy efficiency, and design possibilities.
For most consumers, opting for an LED TV—particularly one with full-array local dimming—offers a noticeable upgrade over older CCFL-backlit LCD models. The improved contrast, color accuracy, and slimmer design enhance the overall viewing experience.
However, it’s important to consider other factors such as budget, viewing environment, and specific use cases like gaming or movie watching. Additionally, exploring newer technologies like OLED or Mini-LED may be worthwhile for those seeking premium performance.
In summary, understanding the difference between LED and LCD televisions empowers buyers to make choices that align with their preferences and ensures satisfaction with their investment in home entertainment technology.
Discover the Future of Television with LumenMatrix
Ready to experience the ultimate in picture quality and innovative display technology? LumenMatrix is at the forefront of LED display solutions, offering a wide array of products from Indoor and Outdoor LED Wall Displays to specialized options like Vehicle and Sports LED Displays. Whether you’re looking to elevate your home entertainment or transform your business’s visual communication, LumenMatrix has the cutting-edge technology to bring your vision to life. Don’t settle for less—check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today and step into a world where clarity, engagement, and design meet to create unforgettable visual experiences.