In an era where digital visuals dominate advertising, entertainment, and information dissemination, LED displays have become a cornerstone technology. From colossal billboards in Times Square to the vibrant video walls at sports arenas, LED displays offer unmatched brightness, clarity, and flexibility. But what exactly makes an LED display tick? This article delves deep into the technology behind LED displays, their types, advantages, and the evolving trends shaping their future.
Understanding LED Display Technology
What Is an LED Display?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. An LED display is a flat panel or flexible surface that uses an array of these diodes to create images, videos, or text. Unlike traditional LCD or plasma screens, LED displays generate their own light, which allows them to produce vivid colors and high contrast even in bright environments.
LED displays can range from small digital watches and smartphone screens to massive outdoor billboards. The core principle remains the same: thousands or millions of tiny LEDs work in unison to form a cohesive image visible to the human eye.
How Do LED Displays Work?
Each LED in a display acts as a pixel or part of a pixel. Depending on the display type, a pixel may consist of one or more LEDs emitting red, green, and blue light. By adjusting the intensity of these LEDs, the display can reproduce a wide spectrum of colors.
The LEDs are arranged in a grid pattern, and a controller processes input signals—such as video or image data—to determine which LEDs light up and at what brightness. This process happens thousands of times per second, creating smooth motion and dynamic visuals.
Key Components of an LED Display
Several components work together to make an LED display function:
- LED Modules: These are the building blocks containing the LEDs arranged in pixels.
- Driver ICs: Integrated circuits that control the current and voltage to each LED, ensuring accurate brightness and color.
- Power Supply: Provides the necessary electrical power to the display.
- Control System: Processes input data and manages the timing and sequencing of LED activation.
- Cabinet/Frame: Holds the modules together, often designed for durability and weather resistance in outdoor applications.
Types of LED Displays
Indoor vs. Outdoor LED Displays
One of the primary distinctions in LED displays is based on their environment of use. Indoor LED displays are designed for controlled lighting conditions and typically have higher pixel density for closer viewing distances. Outdoor LED displays, on the other hand, are built to withstand weather elements and must be exceptionally bright to combat sunlight glare.
For example, an indoor LED screen in a conference room might have a pixel pitch of 1.2mm to 2.5mm, meaning the distance between each LED pixel is very small, allowing for sharp images at close range. Outdoor LED billboards often have pixel pitches of 8mm or more, balancing resolution with visibility from a distance.
Direct View LED vs. LED-Backlit LCD
It is important to differentiate between direct view LED displays and LED-backlit LCD screens. Direct view LED displays use LEDs as the actual pixels forming the image, while LED-backlit LCDs use LEDs only as a backlight behind a liquid crystal panel.
Direct view LEDs offer superior brightness, contrast, and viewing angles, making them ideal for large-scale digital signage and video walls. LED-backlit LCDs are more common in consumer electronics like televisions and monitors due to their cost-effectiveness and image quality in smaller sizes.
MicroLED and MiniLED: The Next Generation
Emerging technologies such as MicroLED and MiniLED are pushing the boundaries of LED display performance. MicroLED displays use microscopic LEDs to create pixels, offering exceptional brightness, color accuracy, and energy efficiency. They also avoid issues like burn-in that affect OLED screens.
MiniLED, meanwhile, refers to LED backlighting with thousands of tiny LEDs behind an LCD panel, improving contrast and local dimming capabilities. Both technologies are gaining traction in premium TVs, smartphones, and professional displays, signaling a shift towards more advanced LED-based solutions.
Advantages of LED Displays
Brightness and Visibility
One of the most significant advantages of LED displays is their outstanding brightness. Outdoor LED billboards can achieve brightness levels exceeding 5,000 nits, ensuring visibility even under direct sunlight. This makes them indispensable for advertising, traffic signage, and public information systems.
Indoor LED displays also benefit from high brightness, which enhances image clarity and reduces eye strain in well-lit environments. The ability to adjust brightness dynamically also contributes to energy savings and longer lifespan.
Color Accuracy and Contrast
LED displays provide excellent color reproduction, thanks to their ability to control individual LEDs precisely. This results in vibrant, true-to-life colors that enhance viewer engagement. Additionally, because LEDs emit light directly, they offer superior contrast ratios compared to traditional LCDs, especially in dark scenes.
Durability and Longevity
LEDs are solid-state devices with no fragile components like filaments or gas, making them highly durable. Outdoor LED displays are typically rated with IP65 or higher for water and dust resistance, allowing them to operate reliably in harsh weather conditions.
Moreover, LEDs have a long operational life, often exceeding 100,000 hours before significant brightness degradation. This translates to years of maintenance-free use, reducing total cost of ownership.
Energy Efficiency
Compared to older display technologies such as plasma or incandescent lighting, LEDs consume significantly less power. Advances in LED chip design and driver electronics have further improved energy efficiency, making LED displays more environmentally friendly and cost-effective to operate.
Applications of LED Displays
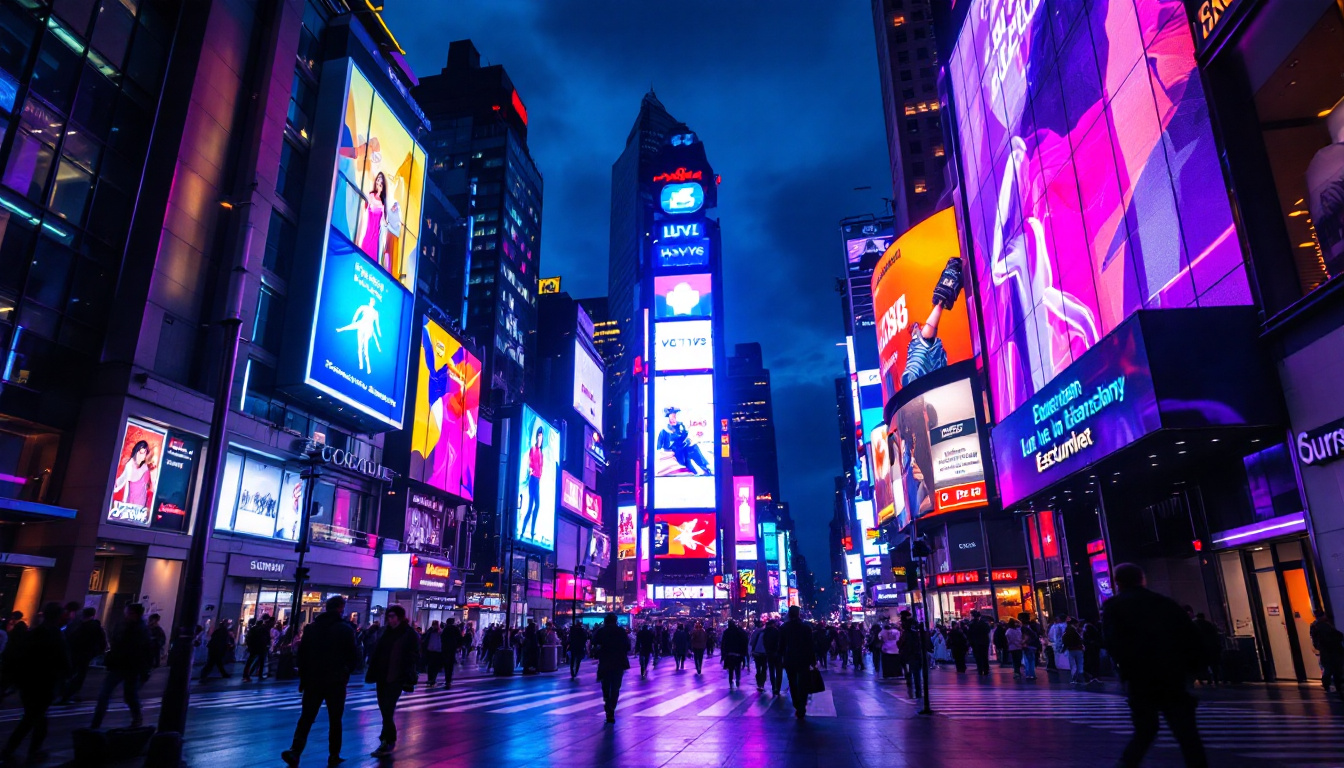
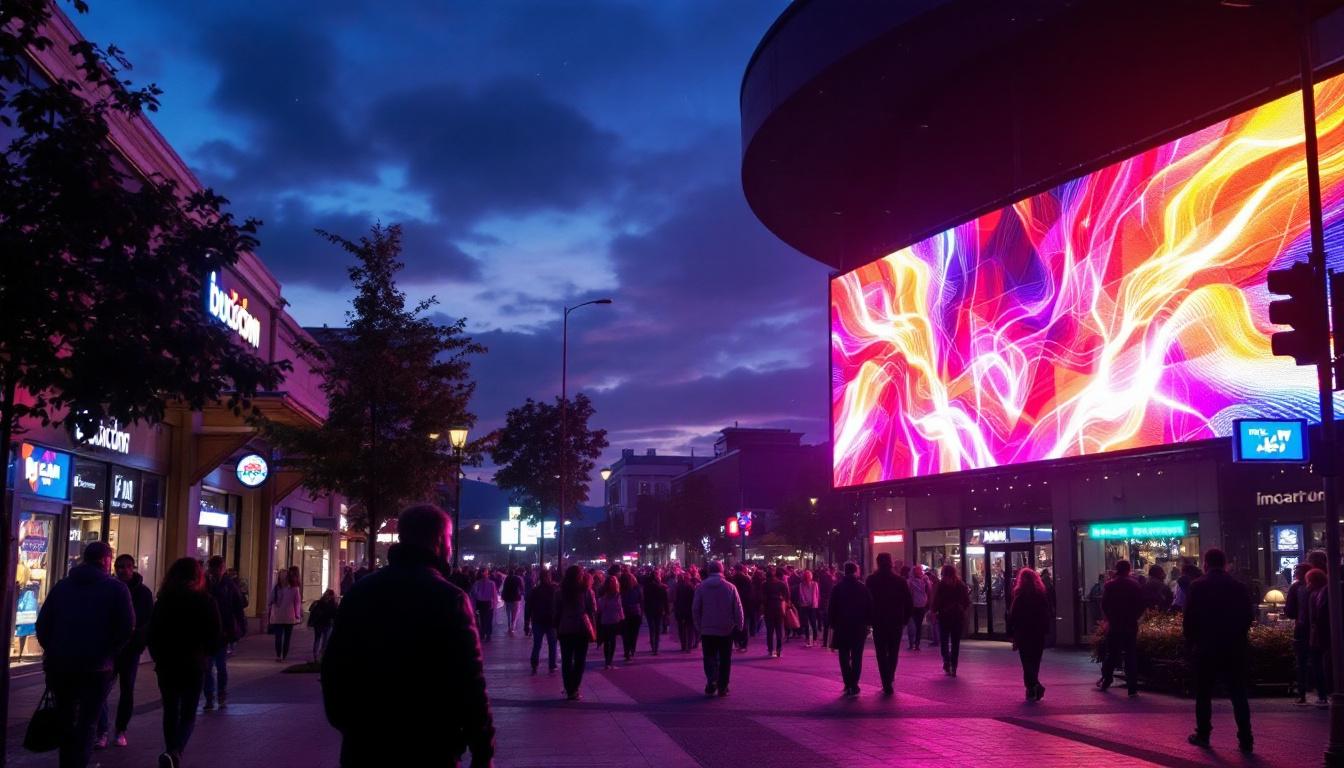
Advertising and Digital Signage
LED displays have revolutionized outdoor and indoor advertising. Their ability to display dynamic, eye-catching content attracts more attention than static billboards. According to industry reports, digital out-of-home advertising using LED displays is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10% through 2028.
Retail stores, shopping malls, and transportation hubs use LED displays to engage customers, promote products, and provide real-time information. The flexibility to update content remotely enables marketers to tailor messages based on time, location, or audience demographics.
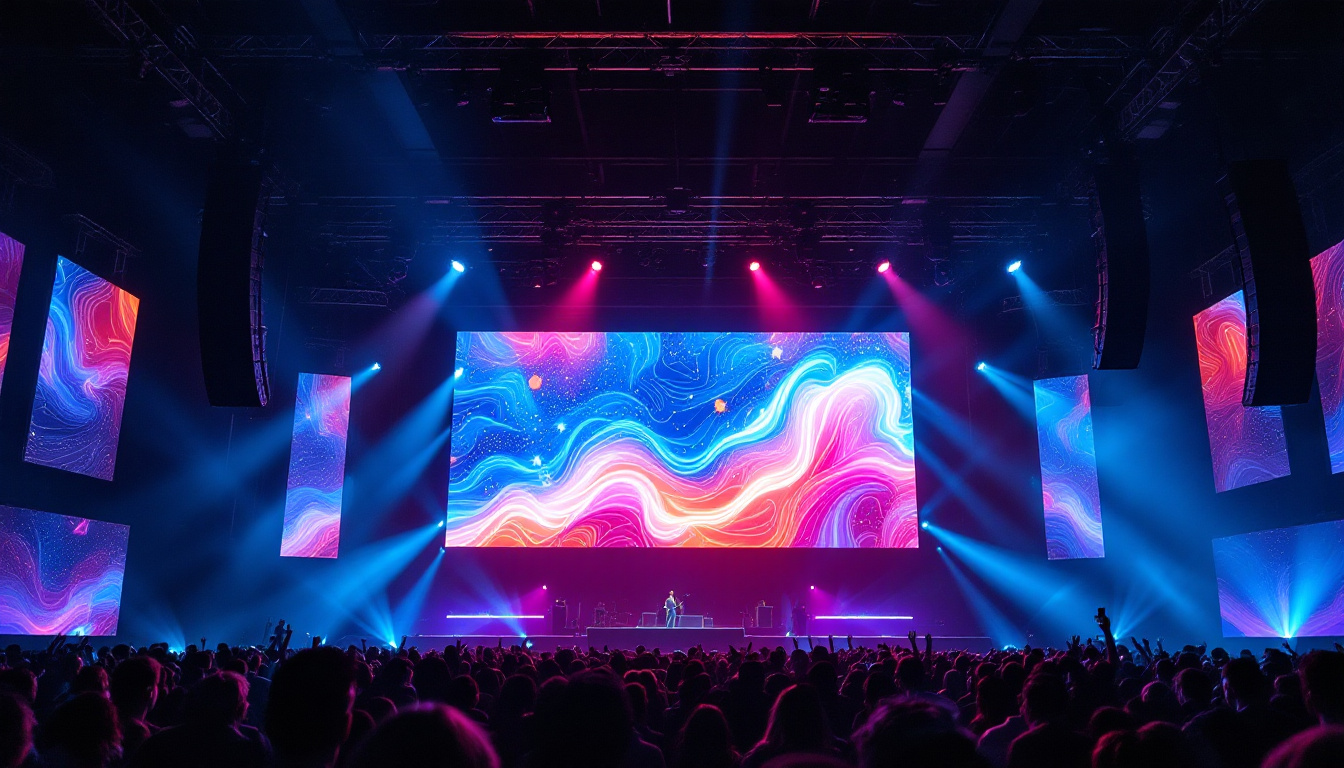
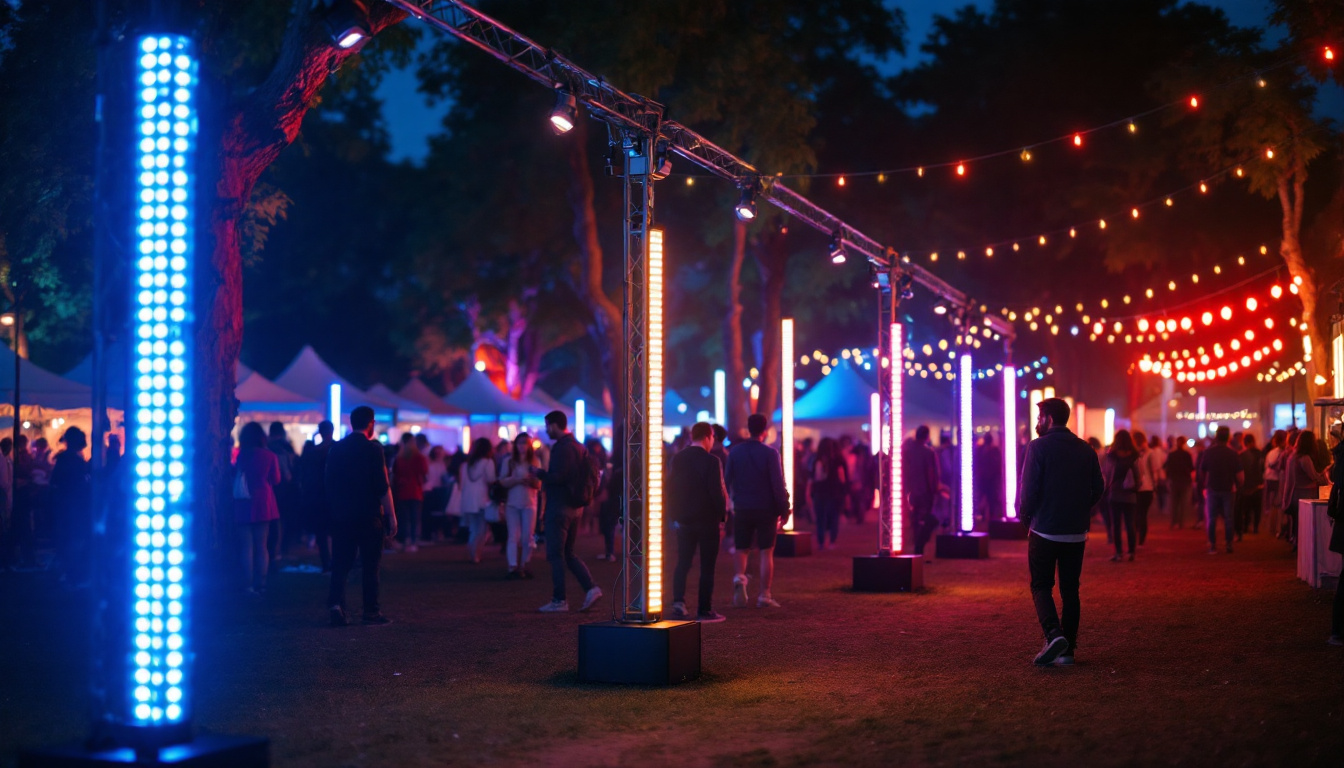
Sports and Entertainment Venues
Stadiums and arenas rely heavily on large LED video walls to enhance the spectator experience. These displays show live game footage, replays, advertising, and interactive content. The high brightness and fast refresh rates ensure visibility and smooth motion, even in large venues with thousands of attendees.
Concerts and theatrical productions also use LED screens for immersive backdrops and visual effects, adding a new dimension to live performances.
Transportation and Public Information
LED displays are widely used in airports, train stations, and bus terminals to provide schedules, alerts, and wayfinding information. Their high visibility and reliability make them ideal for critical communication in high-traffic areas.
Additionally, traffic management systems employ LED signs for variable message signs, speed advisories, and safety warnings, contributing to safer and more efficient roadways.
Corporate and Educational Environments
Corporate offices use LED displays for video conferencing, presentations, and digital notice boards. Educational institutions integrate LED screens into classrooms and auditoriums to enhance learning through multimedia content and interactive sessions.
Challenges and Considerations
Cost and Installation
While LED display prices have decreased significantly over the past decade, high-resolution, large-format LED screens can still represent a substantial investment. Installation requires careful planning, especially for outdoor or curved displays, to ensure structural stability and optimal viewing angles.
Maintenance costs, though generally low, should also be factored in, particularly for outdoor installations exposed to environmental stressors.
Pixel Pitch and Viewing Distance
Choosing the right pixel pitch is critical to achieving the desired image quality. A smaller pixel pitch means higher resolution but also higher cost. For example, a 1.5mm pixel pitch is suitable for indoor displays viewed from a few feet away, while an 8mm pitch might be adequate for an outdoor billboard seen from hundreds of feet.
Understanding the relationship between pixel pitch, viewing distance, and resolution helps optimize both performance and budget.
Environmental Impact
Although LED displays are energy-efficient, their production involves rare earth elements and electronic components that can have environmental consequences. Responsible sourcing, recycling programs, and advances in sustainable manufacturing are essential to mitigate these impacts.
The Future of LED Displays
Flexible and Transparent LED Screens
Innovations in materials and design have led to the development of flexible and transparent LED displays. These can be integrated into windows, curved surfaces, or wearable devices, opening up new possibilities for advertising, architecture, and consumer electronics.
For instance, transparent LED glass panels can transform storefront windows into dynamic displays without obstructing natural light, enhancing both aesthetics and functionality.
Integration with AI and IoT
Smart LED displays equipped with sensors and AI-driven content management systems are becoming more prevalent. These systems can analyze audience demographics, weather conditions, and time of day to deliver personalized and contextually relevant content.
Integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) also enables real-time data feeds, interactive experiences, and remote diagnostics, improving operational efficiency and user engagement.
Higher Resolutions and Energy Efficiency
As MicroLED technology matures, expect LED displays to achieve resolutions rivaling or surpassing OLED and LCD counterparts, with even greater energy savings. This will expand their use in smartphones, laptops, and augmented reality devices, where image quality and power consumption are paramount.
Conclusion
LED displays have transformed the way information and entertainment are delivered across various sectors. Their superior brightness, color accuracy, durability, and versatility make them indispensable in modern digital communication. Understanding the underlying technology, types, and applications helps businesses and consumers make informed decisions when selecting LED display solutions.
With ongoing advancements in MicroLED, flexible designs, and smart integration, LED displays are poised to become even more dynamic and immersive, shaping the future of visual media in exciting ways.
Discover the Future of Visuals with LumenMatrix
Ready to elevate your visual impact? Explore LumenMatrix’s innovative LED display solutions, where cutting-edge technology meets creative design. From vibrant Indoor LED Walls to robust Outdoor displays, and from dynamic Vehicle LED Displays to sleek LED Posters, our range is crafted to captivate and engage your audience. Whether you’re looking to create an immersive sports experience or a customized visual statement, LumenMatrix is your partner in revolutionizing visual communication. Check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today and transform your space into a beacon of digital innovation.