In today’s digital era, screens dominate our daily lives—from smartphones and laptops to massive advertising billboards and stadium displays. Central to these screens is the concept of the pixel, the fundamental building block of any digital image. Among the various display technologies, LED displays have become particularly prominent due to their brightness, energy efficiency, and versatility. This article delves into the world of pixels on LED screens, exploring how LED displays work, their advantages, and their evolving role in modern technology.
Understanding Pixels: The Foundation of Digital Displays
Before diving into LED displays specifically, it’s essential to understand what a pixel is and why it matters. A pixel, short for “picture element,” is the smallest controllable unit of a digital image. When combined in large numbers, pixels create the images and videos we see on screens.
Each pixel typically consists of subpixels that emit red, green, and blue light. By varying the intensity of these subpixels, a wide spectrum of colors can be produced. This RGB color model is the foundation of most digital displays, enabling millions of color variations that bring images to life.
The resolution of a display is determined by the number of pixels it contains horizontally and vertically. For example, a Full HD screen has a resolution of 1920 x 1080 pixels, meaning it contains over two million pixels. The higher the pixel density, measured in pixels per inch (PPI), the sharper and more detailed the image appears.
What is an LED Display?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. An LED display is a flat panel display that uses an array of LEDs as pixels to produce images. These displays can be found in various forms, from small indicator lights to large outdoor billboards.
Unlike traditional LCD screens, which rely on backlighting, LED displays generate their own light. This self-emissive property allows LEDs to produce brighter images with better contrast and deeper blacks. LED technology can be implemented in several ways, including direct-view LED panels and LED-backlit LCDs.
Direct-View LED Displays
Direct-view LED displays consist of thousands or millions of tiny LEDs arranged in a grid. Each LED acts as a pixel or part of a pixel, emitting red, green, or blue light. These displays are commonly used for large-scale applications such as outdoor advertising, sports arenas, and public information screens.
One of the key advantages of direct-view LED displays is their ability to produce extremely high brightness levels, often exceeding 5,000 nits, making them visible even under direct sunlight. Additionally, their modular design allows for flexible sizing and shapes, catering to diverse installation needs.
LED-Backlit LCD Displays
In LED-backlit LCDs, the LEDs serve as a backlight behind a liquid crystal display panel. The LCD controls the light passing through each pixel, while the LED backlight provides illumination. This hybrid approach offers improved energy efficiency and thinner panels compared to traditional cold cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL) backlighting.
Most modern televisions, computer monitors, and smartphone screens use LED-backlit LCD technology. While they don’t achieve the same contrast ratios as direct-view LED displays, they strike a balance between image quality, cost, and power consumption.
How Pixels Work on LED Displays
The operation of pixels on LED displays is a fascinating interplay of electrical engineering and optics. Each pixel is composed of subpixels—typically red, green, and blue LEDs—that combine to form the desired color through additive color mixing.
When an image is displayed, the controlling electronics send signals to each pixel’s subpixels, adjusting their brightness levels. For example, to display pure white, all three subpixels are lit at full intensity. To create yellow, the red and green subpixels are illuminated while the blue remains off or at a low level.
Pixel Pitch and Its Impact on Image Quality
Pixel pitch refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent pixels, usually measured in millimeters. It is a critical factor in determining the resolution and viewing distance of an LED display. Smaller pixel pitch means more pixels per unit area, resulting in higher resolution and finer image detail.
For instance, indoor LED displays often have pixel pitches ranging from 0.9 mm to 4 mm, enabling close-up viewing with crisp images. Outdoor displays, on the other hand, typically have larger pixel pitches (10 mm or more) because they are viewed from greater distances where fine detail is less critical.
Refresh Rate and Color Accuracy
The refresh rate of an LED display indicates how many times per second the image is updated, measured in hertz (Hz). Higher refresh rates reduce flicker and motion blur, enhancing the viewing experience, especially for fast-moving content like sports or video games.
Color accuracy depends on the quality of the LEDs and the calibration of the display. Advances in LED technology, such as quantum dot enhancements and improved phosphor coatings, have significantly broadened the color gamut and improved color fidelity in recent years.
Advantages of LED Displays Over Other Technologies
LED displays offer several compelling advantages that have driven their widespread adoption across various industries. Understanding these benefits helps explain why LED technology continues to evolve and dominate the display market.
Brightness and Visibility
One of the standout features of LED displays is their exceptional brightness. Direct-view LED panels can achieve brightness levels well above 5,000 nits, far surpassing most LCD and OLED displays. This makes them ideal for outdoor environments where sunlight can wash out other types of screens.
Enhanced visibility under diverse lighting conditions ensures that content remains clear and engaging, whether it’s a digital billboard on a busy street or a scoreboard in a sunlit stadium.
Energy Efficiency and Longevity
LEDs are inherently energy-efficient, converting a higher percentage of electrical energy into visible light compared to traditional lighting technologies. This efficiency translates to lower power consumption for LED displays, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Moreover, LEDs have a long operational lifespan, often exceeding 50,000 hours of use. This durability minimizes maintenance and replacement expenses, particularly important for large-scale installations.
Design Flexibility and Scalability
LED displays can be manufactured in a wide range of sizes and shapes, from small wearable devices to massive curved or irregularly shaped video walls. Their modular nature allows for easy scalability and customization, accommodating unique architectural and branding requirements.
This design flexibility has led to creative applications, such as transparent LED glass walls, flexible LED screens integrated into clothing, and interactive digital signage.
Applications of LED Displays in Modern Life
LED display technology has permeated numerous sectors, revolutionizing how information and entertainment are delivered. The versatility and performance of LED screens make them a preferred choice in many contexts.
Advertising and Digital Signage
Outdoor advertising has been transformed by LED billboards, which offer dynamic, eye-catching content that can be updated in real time. According to industry reports, the global digital signage market is projected to reach over $31 billion by 2027, driven largely by LED technology.
Retailers and businesses use LED displays to attract customers, promote products, and enhance brand visibility. The ability to display vivid animations and videos makes LED signage far more engaging than static posters.
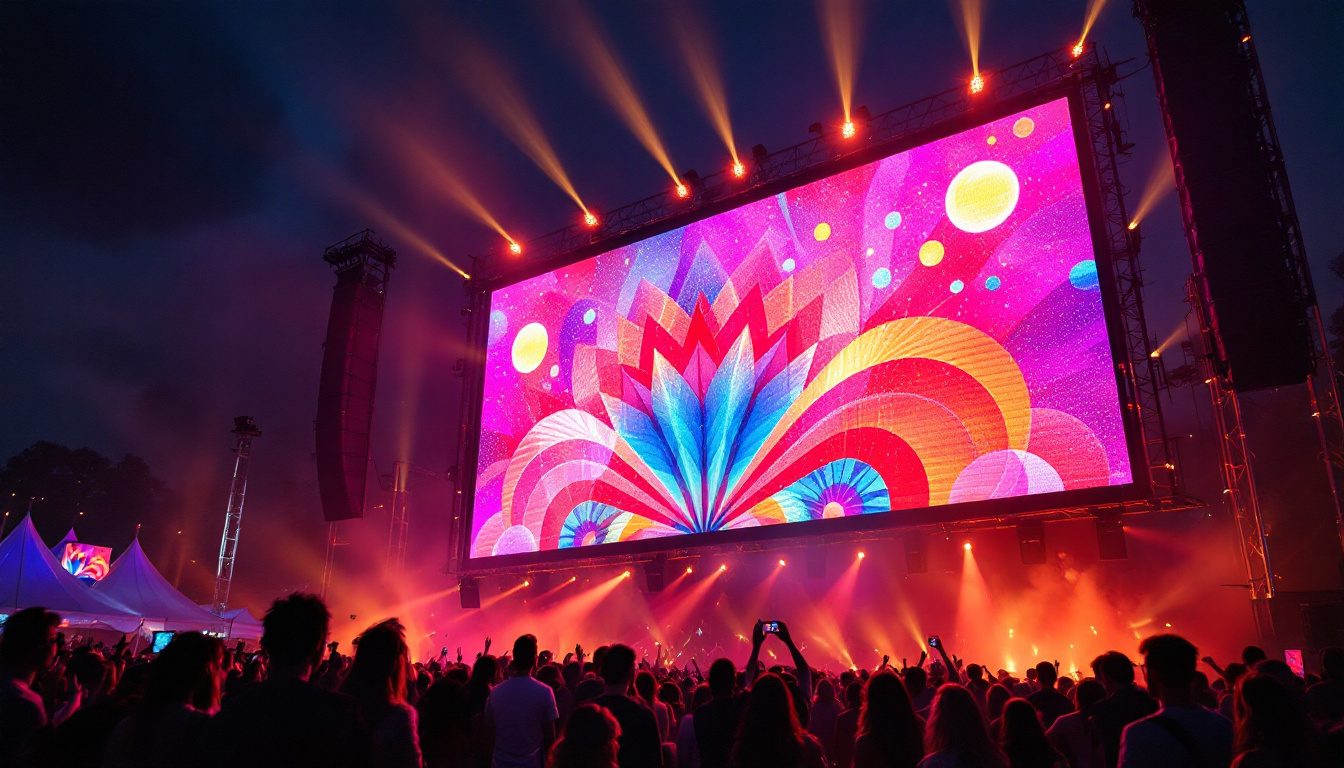
Entertainment and Sports Venues
Stadiums and concert venues rely on large LED screens to provide spectators with close-up views, replays, and interactive content. These displays must deliver high brightness and fast refresh rates to keep pace with live action.
LED walls are also a staple in television studios and theaters, offering immersive backgrounds and special effects that enhance production quality.
Consumer Electronics
From smartphones to televisions, LED technology plays a crucial role in delivering vibrant, energy-efficient displays. The ongoing improvements in LED-backlit LCDs and the emergence of microLED technology promise even better image quality and power savings in future devices.
Transportation and Public Information
LED displays are widely used in airports, train stations, and bus terminals to provide real-time scheduling and safety information. Their reliability and visibility ensure passengers stay informed in busy environments.
The Future of LED Display Technology
Innovation in LED technology continues at a rapid pace, promising exciting developments that will further enhance display performance and applications.
MicroLED and MiniLED Advances
MicroLED technology involves microscopic LEDs that serve as individual pixels, offering superior brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency compared to traditional LEDs. This technology is poised to challenge OLED displays in high-end consumer electronics by combining the best attributes of both.
MiniLEDs, which are smaller than conventional LEDs but larger than microLEDs, are already being used to improve backlighting in LCD panels, resulting in better contrast and HDR performance.
Flexible and Transparent Displays
Research into flexible LED displays is enabling screens that can bend, fold, or roll, opening new possibilities for wearable devices, foldable phones, and innovative advertising formats. Transparent LED displays, which allow light to pass through while showing images, are being integrated into windows and glass facades for augmented reality and architectural applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
As LED displays become more widespread, manufacturers are focusing on reducing environmental impact through recyclable materials, lower power consumption, and longer product lifecycles. Sustainable design practices are increasingly important to consumers and regulatory bodies alike.
Conclusion
From the smallest smartphone screen to the largest outdoor billboard, pixels on LED displays form the visual foundation of modern digital communication. Understanding how these pixels work and the advantages of LED technology provides insight into why LED displays have become ubiquitous across industries.
With ongoing advancements in microLED, flexible designs, and sustainability, LED display technology is set to continue shaping the future of visual media. Whether for advertising, entertainment, or everyday devices, LED displays offer a powerful combination of brightness, efficiency, and versatility that meets the demands of today’s dynamic digital world.
Discover Cutting-Edge LED Display Solutions with LumenMatrix
Ready to elevate your visual experience with the latest in LED technology? Look no further than LumenMatrix, a pioneer in crafting LED display modules that transform any space into a dynamic visual spectacle. Whether you’re in need of an Indoor LED Wall Display for your business, an Outdoor LED Wall Display for impactful advertising, a Vehicle LED Display for mobile marketing, or any of our other innovative solutions like LED Sports Displays and Custom LED Displays, LumenMatrix has you covered. Embrace the future of visual communication and check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today to captivate your audience and amplify your message like never before.