What Does LCD: LED Display Explained
In today’s technology-driven world, display screens are everywhere—from smartphones and laptops to televisions and digital signage. Among the many types of display technologies, LCD and LED displays are the most prevalent. However, the terminology can often be confusing, especially when terms like “LCD LED display” are used interchangeably. This article aims to clarify what an LCD: LED display actually means, how these technologies work, and why understanding the differences is important for consumers and professionals alike.
Understanding the Basics: What is an LCD?
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display. It is a flat-panel display technology that uses liquid crystals to modulate light and produce images. Unlike older cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, LCDs are thin, lightweight, and energy-efficient, making them the standard for most modern screens.
At its core, an LCD screen consists of several layers: two polarized panels with liquid crystals sandwiched between them. When an electric current passes through the crystals, they align in such a way that controls the amount of light passing through each pixel. However, LCDs do not emit light themselves; they rely on an external light source called a backlight to illuminate the display.
How LCDs Work
The liquid crystals in the display act like shutters, opening and closing to allow varying degrees of light to pass through. This modulation of light creates the images you see on the screen. Because the crystals don’t emit light, the quality of the backlight is crucial for brightness, contrast, and color accuracy. Various types of backlighting technologies, such as LED (Light Emitting Diode) and CCFL (Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamp), have been developed to enhance the performance of LCDs. LED backlighting, in particular, has gained popularity due to its ability to provide better energy efficiency and a wider color gamut compared to traditional CCFLs.
Common Uses of LCD Technology
LCD technology is widely used in devices such as computer monitors, televisions, smartphones, digital watches, and instrument panels. Its affordability, low power consumption, and ability to produce sharp images have made it a dominant display technology worldwide. In addition to consumer electronics, LCDs are also employed in various industrial applications, including medical imaging devices, automotive displays, and even in the field of advertising through digital signage. The versatility of LCDs allows for customization in size and resolution, catering to both small handheld devices and large-format displays used in public spaces.
Moreover, the ongoing advancements in LCD technology have led to the development of specialized types, such as IPS (In-Plane Switching) and TN (Twisted Nematic) panels. IPS panels are known for their superior color reproduction and wider viewing angles, making them ideal for professional graphic design and photography. On the other hand, TN panels are favored for their faster response times, which are beneficial for gaming and fast-paced video content. As the demand for high-quality displays continues to rise, innovations in LCD technology are expected to evolve, further enhancing user experience across various platforms.
What is LED and How Does it Relate to LCD?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode, a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. In the context of displays, LEDs are primarily used as backlighting sources for LCD panels. This is where the term “LED display” can cause confusion, as it often refers to an LCD screen illuminated by LED backlights rather than a display made entirely of LEDs.
LED Backlighting in LCD Displays
Traditional LCD screens used cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs) for backlighting. While effective, CCFLs consume more power and offer less precise control over brightness and color. The introduction of LED backlighting revolutionized LCD displays by providing several benefits:
- Improved Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume less power than CCFLs, extending battery life in portable devices and reducing electricity costs for larger displays.
- Better Brightness and Contrast: LEDs can achieve higher brightness levels and more precise dimming, enhancing image quality.
- Thinner and Lighter Designs: LED backlights are smaller, allowing manufacturers to create slimmer screens.
- Longer Lifespan: LEDs generally last longer than CCFLs, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Types of LED Backlighting
There are two main types of LED backlighting used in LCD displays:
- Edge-Lit LED: LEDs are placed along the edges of the screen, and light is spread across the display using light guides. This design allows for ultra-thin panels but may have less uniform brightness.
- Direct or Full-Array LED: LEDs are placed directly behind the LCD panel in a grid pattern. This allows for better control of local dimming zones, resulting in improved contrast and black levels.
Is an LED Display the Same as an LCD Display?
Despite common usage, an LED display is not the same as an LCD display. The confusion arises because many LCD screens use LED backlights, leading manufacturers and retailers to market these products as “LED TVs” or “LED displays.”
True LED Displays
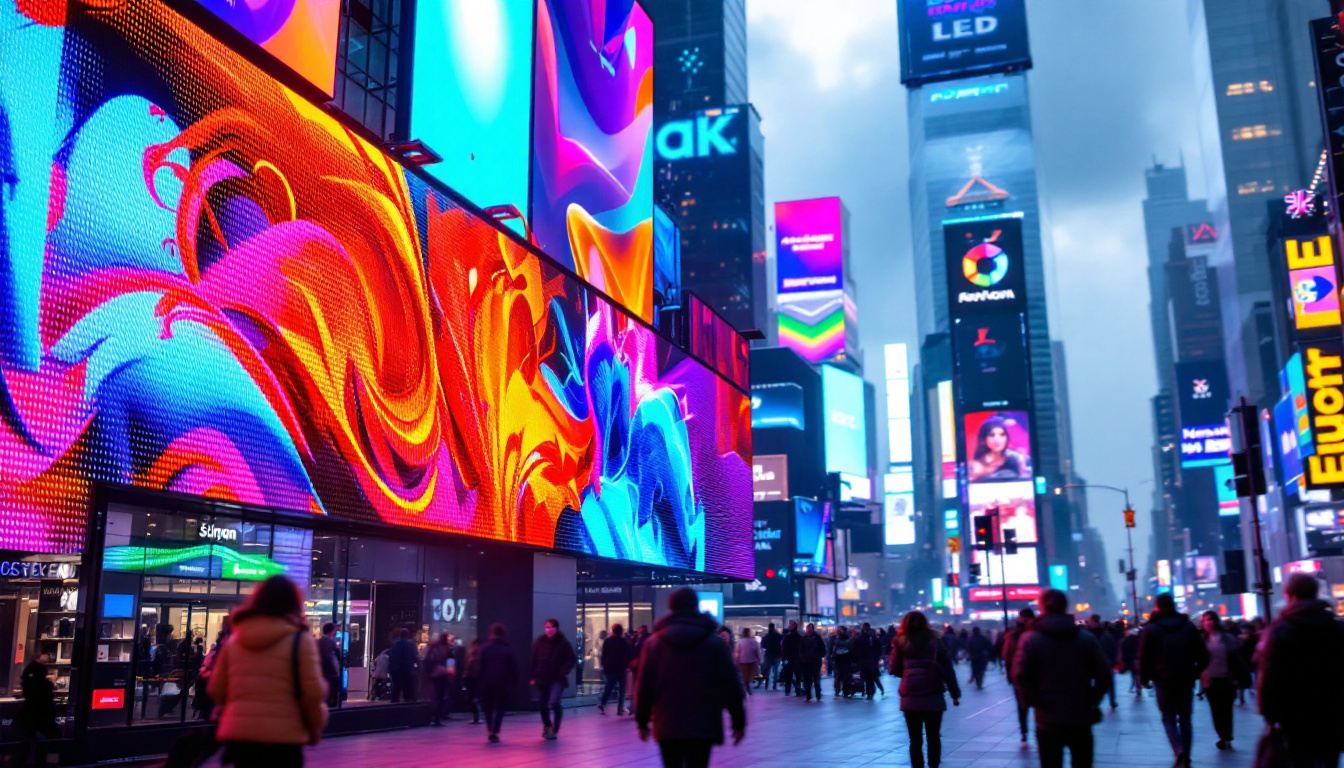
True LED displays, often referred to as direct-view LED displays, are made up of thousands of tiny LEDs that act as individual pixels. These displays emit their own light, eliminating the need for a backlight. They are commonly used in large-scale applications such as stadium screens, billboards, and some high-end televisions.
Direct-view LED displays offer several advantages:
- Superior Brightness: They can achieve extremely high brightness levels, making them ideal for outdoor use.
- Excellent Contrast: Individual LEDs can be turned off completely, producing true blacks.
- Wide Viewing Angles: The light emitted directly from LEDs ensures consistent color and brightness from various angles.
LCD with LED Backlighting vs. True LED Displays
In contrast, LCD displays with LED backlighting rely on the liquid crystal layer to modulate light from the LEDs behind or around the screen. While this combination provides excellent image quality and energy efficiency, it cannot match the contrast and brightness levels of direct-view LED displays.
Understanding this distinction is crucial when purchasing displays for specific needs, as the technology impacts performance, cost, and suitability for different environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LCD: LED Displays
LCD displays with LED backlighting have become the standard for most consumer electronics, but like any technology, they have their strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages
- Energy Efficiency: LED backlighting consumes less power than older CCFL backlights, making devices more energy-efficient.
- Thin and Lightweight: The compact size of LEDs allows for slimmer and lighter display designs.
- Improved Image Quality: LED backlights provide better brightness and contrast control, enhancing overall picture quality.
- Longer Lifespan: LEDs generally last longer than CCFLs, reducing the need for replacements.
- Environmentally Friendly: LEDs contain no mercury, unlike CCFLs, making them safer for disposal and recycling.
Disadvantages
- Limited Contrast Compared to OLED: While LED-backlit LCDs have improved contrast, they still cannot achieve the perfect blacks of OLED displays.
- Viewing Angles: Some LCD panels may exhibit color shifting or reduced brightness when viewed from extreme angles.
- Backlight Bleeding: Uneven backlighting can cause light to leak around the edges or corners, affecting image uniformity.
- Response Time: LCDs typically have slower response times than OLEDs, which can impact fast-moving images in gaming or sports.
Emerging Technologies and the Future of Displays
The display industry continues to evolve rapidly, with new technologies challenging the dominance of LCD: LED displays. Understanding these developments helps consumers and professionals make informed decisions.
OLED and MicroLED
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) displays differ fundamentally from LCD: LED displays because each pixel emits its own light. This results in superior contrast, faster response times, and wider viewing angles. However, OLEDs can be more expensive and have potential issues with burn-in over time.
MicroLED technology, still emerging, combines the self-emissive benefits of OLED with the durability and brightness of LEDs. MicroLED displays promise exceptional image quality, energy efficiency, and longevity, potentially becoming the next big leap in display technology.
Mini-LED Backlighting
Mini-LED is an advancement in LED backlighting for LCD panels. By using thousands of tiny LEDs, mini-LED backlights offer more precise local dimming, better contrast ratios, and improved brightness compared to traditional LED backlighting. This technology bridges the gap between conventional LCD: LED displays and OLEDs in terms of picture quality.
Quantum Dot Displays
Quantum dot technology enhances LCD displays by adding a layer of semiconductor nanocrystals that emit pure, highly saturated colors when illuminated by the backlight. This results in wider color gamuts and more vibrant images, making quantum dot LCDs popular in premium televisions.
How to Choose the Right Display Technology
When selecting a display, understanding the differences between LCD, LED, and other technologies is essential. The choice depends on factors such as usage, budget, and desired image quality.
Consider Your Usage
For everyday computing, office work, and casual media consumption, LCD displays with LED backlighting offer excellent value, energy efficiency, and image quality. For gamers or video professionals, displays with faster response times and better color accuracy may be preferable.
Budget and Longevity
LCD: LED displays tend to be more affordable and have longer lifespans compared to OLEDs. However, if budget allows and superior image quality is a priority, OLED or advanced LCD variants like mini-LED or quantum dot displays might be worth considering.
Viewing Environment
Bright environments benefit from displays with higher brightness levels, such as those with LED or mini-LED backlighting. For dark rooms, displays with better contrast and black levels, like OLEDs, provide a more immersive viewing experience.
Conclusion
The term “LCD: LED display” refers to an LCD screen illuminated by LED backlighting—a combination that has become the industry standard due to its balance of affordability, energy efficiency, and image quality. While true LED displays exist, they are typically reserved for specialized applications and differ significantly from the LCD: LED technology found in most consumer electronics.
As display technologies continue to advance, options like OLED, mini-LED, and quantum dot-enhanced LCDs offer exciting improvements in picture quality and performance. Understanding the distinctions between these technologies empowers consumers to make informed choices tailored to their specific needs and environments.
Ultimately, whether it’s for work, entertainment, or professional use, knowing what an LCD: LED display entails helps navigate the complex landscape of modern screens and ensures the best viewing experience possible.
Discover Cutting-Edge Display Solutions with LumenMatrix
As you consider the vast landscape of display technologies for your personal or professional needs, LumenMatrix stands at the forefront of LED innovation. With a commitment to revolutionizing visual communication, LumenMatrix offers an extensive range of LED display modules designed to elevate brand presence and captivate audiences. From Indoor and Outdoor LED Wall Displays to specialized solutions like Vehicle LED Displays, LED Sports Displays, and even Custom LED Displays, our products are crafted to deliver unparalleled visual experiences. Embrace the future of display technology and check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions to find the perfect fit for your message and space.