What Is The LCD: LED Display Explained
The world of display technology has evolved significantly over the past few decades, leading to the emergence of various types of screens that enhance our viewing experiences. Among these technologies, LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and LED (Light Emitting Diode) displays have become the most prevalent in consumer electronics. While often mentioned together, understanding their differences and how they work is essential for making informed decisions when purchasing devices. This article delves into the intricacies of LCD and LED displays, exploring their features, advantages, and applications.
Understanding LCD Technology
LCD technology utilizes liquid crystals to modulate light and produce images. The fundamental principle behind an LCD is the manipulation of light through liquid crystals, which can change their orientation when an electric current is applied. This property allows LCDs to control the amount of light that passes through them, creating images on the screen.
How LCDs Work
At the core of an LCD is a layer of liquid crystals sandwiched between two polarizing filters. When light passes through the first filter, it becomes polarized. The liquid crystals then twist the light as it passes through, and the second filter determines how much light reaches the viewer’s eyes. By varying the electric current applied to the liquid crystals, different levels of light can be allowed through, thus creating various colors and images on the screen.
LCDs typically require a backlight to illuminate the display, as the liquid crystals themselves do not emit light. This backlighting is usually provided by fluorescent lamps or LED lights, which brings us to the next point of discussion. The choice of backlighting technology can significantly influence the display’s brightness, energy efficiency, and overall color performance. For instance, LED backlighting has become increasingly popular due to its ability to provide higher brightness levels while consuming less power compared to traditional fluorescent options. Additionally, advancements in local dimming technology allow for improved contrast ratios by selectively dimming or brightening specific areas of the screen, enhancing the viewing experience for movies and games alike.
Types of LCD Displays
There are several types of LCD displays available, each designed for specific applications and user needs. The most common types include:
- Twisted Nematic (TN): Known for their fast response times and low production costs, TN panels are often used in gaming monitors. However, they have limited viewing angles and color reproduction compared to other types.
- In-Plane Switching (IPS): IPS panels offer superior color accuracy and wider viewing angles, making them ideal for professional graphic design and photography. They tend to be more expensive than TN panels.
- Vertical Alignment (VA): VA panels provide excellent contrast ratios and deep blacks, making them suitable for watching movies. However, they may have slower response times compared to TN and IPS panels.
Beyond these standard types, there are also specialized LCD technologies designed for niche markets. For example, Super LCD (SLCD) and Advanced Fringe Field Switching (AFFS) are variations that aim to improve upon the limitations of traditional LCDs, such as enhancing color reproduction and reducing motion blur. Additionally, some manufacturers have developed hybrid technologies that combine the best features of different LCD types, catering to users who require both high-speed performance and vibrant color accuracy. These innovations continue to push the boundaries of what LCD technology can achieve, making it a versatile choice for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to professional displays.
The Rise of LED Technology
LED technology represents a significant advancement in display technology, primarily in terms of backlighting for LCDs. While the term “LED display” is often used interchangeably with “LCD,” it is essential to clarify that LED refers to the type of backlighting used in an LCD display rather than a distinct display technology.
LED Backlighting Explained
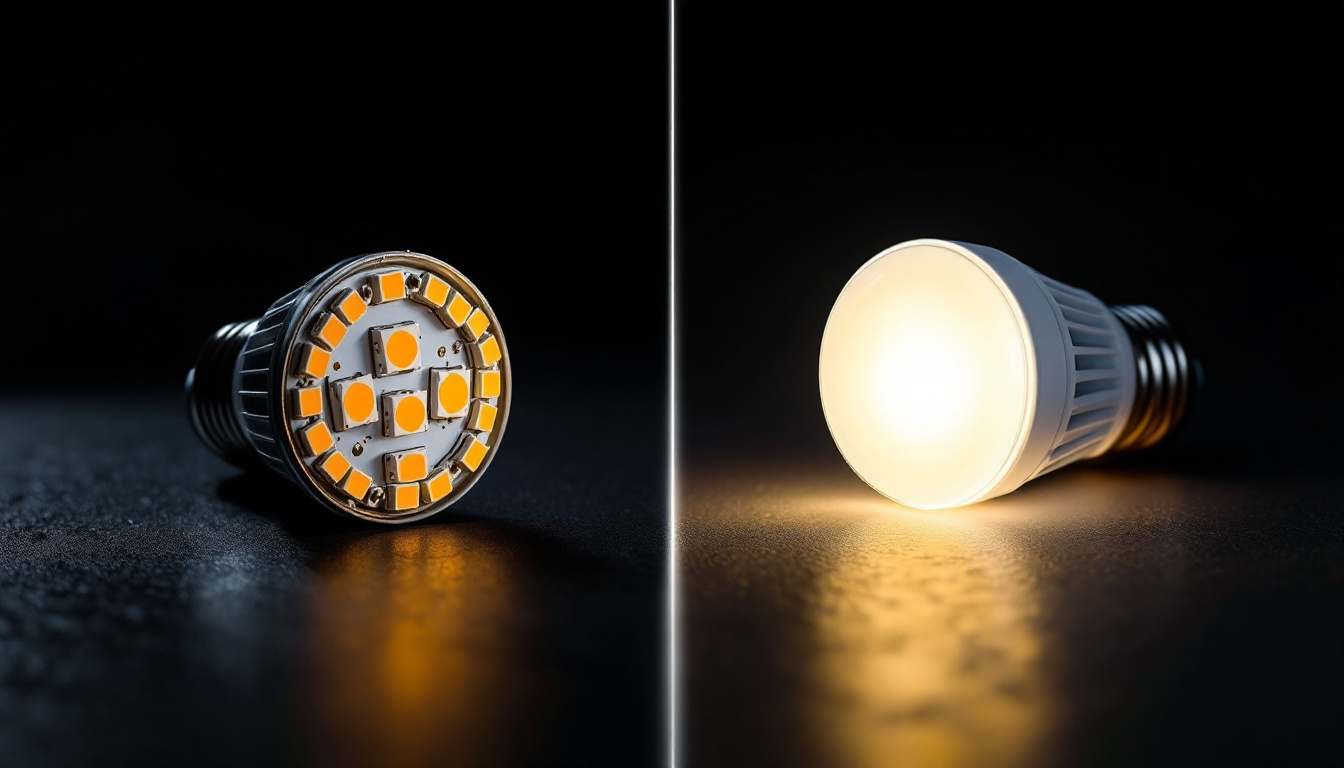
In an LED-backlit LCD, the traditional fluorescent backlighting is replaced with LEDs. This change enhances the display’s brightness, energy efficiency, and overall picture quality. There are two main types of LED backlighting:
- Edge-Lit LED: In this configuration, LEDs are placed around the edges of the screen, allowing for a thinner profile. While this design can be more aesthetically pleasing, it may result in uneven lighting and less vibrant colors.
- Full-Array LED: Full-array backlighting uses a grid of LEDs behind the entire screen, providing more uniform brightness and better contrast. This technology often includes local dimming features, which enhance black levels and overall image quality.
Advantages of LED Displays
LED displays offer several advantages over traditional LCDs with fluorescent backlighting:
- Improved Energy Efficiency: LEDs consume less power than traditional fluorescent lamps, making LED displays more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
- Brighter Images: LED backlighting allows for higher brightness levels, resulting in more vivid and dynamic images, particularly in well-lit environments.
- Longer Lifespan: LEDs have a longer operational life compared to fluorescent bulbs, reducing the need for replacements and maintenance.
In addition to these advantages, LED technology has also paved the way for innovations such as high dynamic range (HDR) imaging. HDR enhances the contrast and color range of images, allowing for a more lifelike viewing experience. By utilizing advanced LED backlighting techniques, displays can achieve deeper blacks and brighter whites, making scenes appear more realistic and immersive. This is particularly beneficial for applications in gaming, film, and photography, where color accuracy and detail are paramount.
Moreover, the versatility of LED technology extends beyond just televisions and monitors. It has found applications in various fields, including automotive lighting, architectural illumination, and even street lighting. The ability to control brightness and color temperature with precision has made LEDs a popular choice for creating dynamic lighting environments. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications that leverage the unique properties of LED lighting, further enhancing our visual experiences in everyday life.
Comparing LCD and LED Displays
While both LCD and LED displays share similarities, understanding their differences is crucial for consumers looking to make informed choices. Below are some key points of comparison:
Image Quality
When it comes to image quality, LED displays generally outperform traditional LCDs due to their superior backlighting technology. Full-array LED displays, in particular, provide better contrast ratios and more accurate colors, making them ideal for viewing high-definition content. This enhanced color accuracy is particularly beneficial for photographers and graphic designers who require precise color representation in their work. Moreover, the ability of LED displays to achieve deeper blacks and brighter whites contributes to a more immersive viewing experience, especially in dark environments where contrast can make a significant difference.
Energy Consumption
Energy efficiency is another area where LED displays shine. The lower power consumption of LEDs compared to traditional fluorescent backlighting means that LED displays not only save on electricity bills but also have a smaller carbon footprint. This is particularly relevant in today’s eco-conscious market, where consumers are increasingly aware of their environmental impact. Additionally, many LED displays come with energy-saving features such as automatic brightness adjustment, which further enhances their efficiency and reduces energy waste during use.
Cost Considerations
While LED displays offer numerous benefits, they often come at a higher price point than standard LCD displays. Consumers should weigh their budget against their desired features and applications when making a decision. It’s also worth noting that the initial investment in an LED display can lead to long-term savings due to lower energy costs and potentially longer lifespan. As technology advances, prices for LED displays have been gradually decreasing, making them more accessible to a wider range of consumers. Furthermore, many manufacturers offer warranties and support for LED products, providing additional peace of mind for buyers concerned about their investment.
Applications of LCD and LED Displays
Both LCD and LED displays have found their way into a variety of applications, from consumer electronics to commercial use. Understanding where each type excels can help consumers and businesses make informed choices.
Consumer Electronics
LCD displays are commonly found in televisions, computer monitors, and laptops. Their versatility and affordability make them a popular choice for everyday use. LED displays, particularly those with full-array backlighting, are increasingly becoming the standard for high-end televisions and monitors, offering superior picture quality for home entertainment.
Commercial Use
In commercial settings, both LCD and LED displays are utilized for digital signage, advertising, and information displays. LED displays are often favored in outdoor applications due to their brightness and visibility in direct sunlight. Conversely, LCDs are more commonly used in indoor settings where space and budget constraints are considerations.
Future Trends in Display Technology
The landscape of display technology is continually evolving, with innovations on the horizon that promise to enhance both LCD and LED displays further. Some emerging trends include:
OLED Technology
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) technology is gaining traction as a potential alternative to traditional LCD and LED displays. OLED panels emit their own light, eliminating the need for backlighting and allowing for thinner designs, better contrast, and more vibrant colors. As production costs decrease, OLED technology may become more accessible to consumers.
MicroLED Displays
MicroLED technology is another exciting development, offering the benefits of OLED without some of its drawbacks, such as burn-in issues. MicroLED displays consist of tiny individual LEDs that can be turned on or off independently, providing exceptional contrast and color accuracy. This technology is still in its infancy but holds great promise for the future of display technology.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the differences between LCD and LED displays is crucial for consumers navigating the ever-evolving world of display technology. While LCDs have been a staple in consumer electronics for years, the advent of LED backlighting has significantly improved their performance and visual quality. As technology continues to advance, new innovations like OLED and MicroLED are set to redefine our viewing experiences further.
Whether one is looking for a budget-friendly option for everyday use or a high-end display for professional applications, there is a display technology available to meet those needs. By staying informed about the latest developments in display technology, consumers can make choices that enhance their viewing experiences and meet their specific requirements.
Explore Cutting-Edge LED Displays with LumenMatrix
Ready to elevate your visual experience with the latest in LED display technology? LumenMatrix is at the forefront of innovation, offering a diverse range of LED display solutions tailored to your needs. From captivating Indoor and Outdoor LED Wall Displays to dynamic Vehicle and Sports LED Displays, and even customizable options like Floor and Custom LED Displays, LumenMatrix has it all. Embrace the future of visual communication with our All-in-One and Transparent LED Displays that promise to enhance engagement and transform your space. Don’t just take our word for it; check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today and see the difference for yourself!