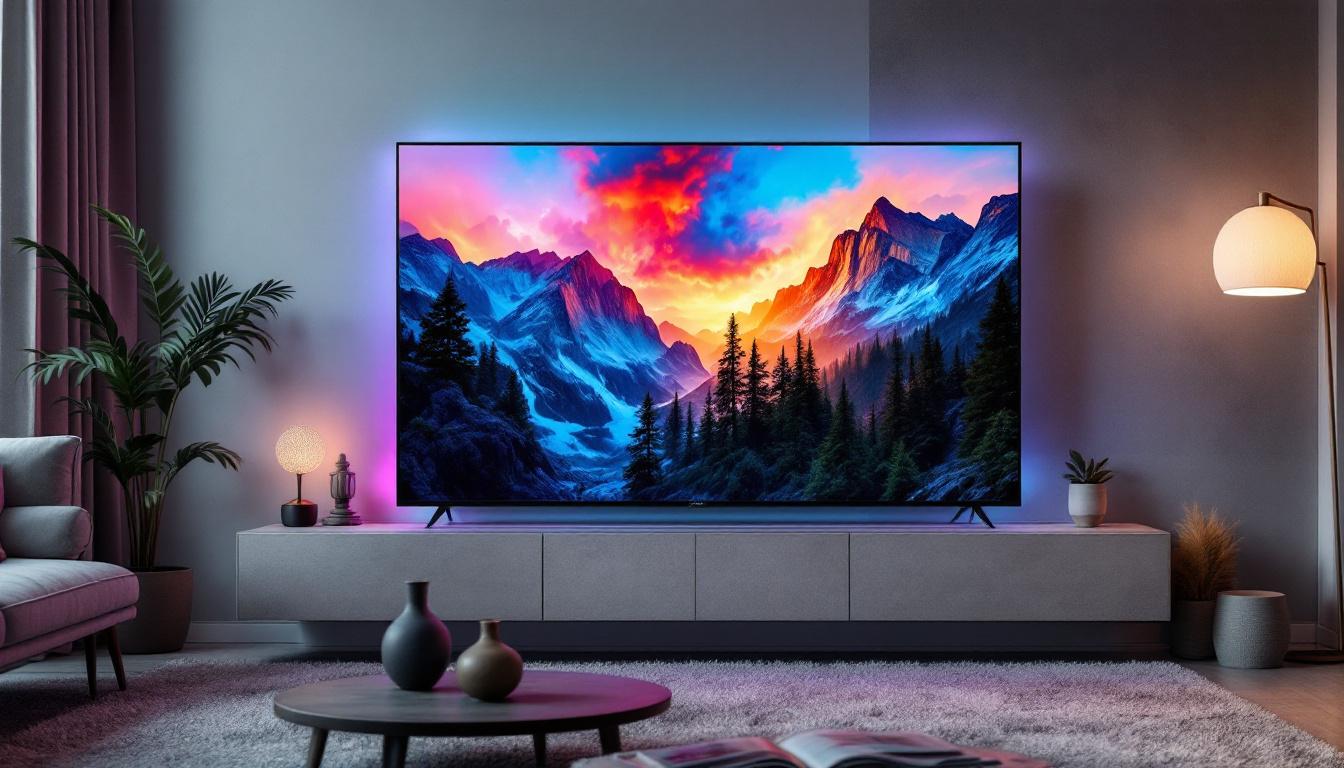
In the ever-evolving world of television technology, understanding the types of TV screens available is essential for making an informed purchase. Among the various display technologies, LED TVs have become the most popular choice for consumers worldwide. But what exactly is an LED display, and how does it compare to other types of TV screens? This article delves deep into the world of LED displays, explaining their technology, advantages, drawbacks, and how they fit into the broader landscape of television screens.
Understanding LED Display Technology
What Does LED Mean?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. In the context of TVs, an LED display refers to a type of LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) television that uses LEDs as its backlighting source. Unlike traditional LCD TVs that used cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs) for backlighting, LED TVs employ tiny light-emitting diodes to illuminate the screen.
This shift to LED backlighting has been a significant advancement, offering better energy efficiency, thinner panels, and improved picture quality. However, it is important to note that LED TVs are essentially LCD TVs with LED backlights, not a completely different display technology like OLED or Plasma. The evolution of LED technology has also led to the development of various display types, such as QLED and Mini-LED, which further enhance color accuracy and brightness, making the viewing experience more immersive.
How Does an LED TV Work?
At the core of an LED TV is the LCD panel, which manipulates light to create images. The LEDs provide the light source behind or around the edges of this panel. When electricity passes through the LEDs, they emit light that passes through the liquid crystals and color filters to produce the images seen on the screen. This process allows for a wide range of colors and brightness levels, contributing to the vividness of the images displayed.
There are two primary types of LED backlighting used in TVs:
- Edge-Lit LED: LEDs are placed along the edges of the screen, and light is diffused across the panel. This design allows for very thin TVs but can sometimes result in uneven lighting.
- Full-Array LED: LEDs are arranged in a grid directly behind the LCD panel. This setup allows for local dimming, where specific zones can be dimmed or brightened independently, enhancing contrast and black levels.
In addition to these backlighting techniques, advancements in technology have led to the incorporation of HDR (High Dynamic Range) capabilities in many LED TVs. HDR enhances the contrast between the brightest whites and the darkest blacks, providing a more dynamic range of colors and making images appear more lifelike. This feature is particularly beneficial for viewing content with rich visuals, such as nature documentaries or action-packed films, where detail in both shadows and highlights is crucial for an engaging experience.
Moreover, the integration of smart technology into LED TVs has transformed the way viewers consume content. With built-in Wi-Fi and access to streaming services, users can enjoy a plethora of shows and movies without the need for additional devices. This convenience has made LED TVs not just a display option, but a central hub for home entertainment, allowing for seamless integration with other smart devices and enhancing the overall user experience.
Advantages of LED TVs
Energy Efficiency and Longevity
One of the most significant benefits of LED TVs is their energy efficiency. Compared to older CCFL-backlit LCDs and plasma TVs, LED TVs consume less power, which can reduce electricity bills and environmental impact. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, LED TVs can use up to 40% less energy than CCFL LCD TVs.
Additionally, LEDs have a longer lifespan than traditional backlighting methods. An LED TV can typically last between 60,000 to 100,000 hours of viewing, which translates to many years of use before any noticeable degradation.
Improved Picture Quality
LED backlighting enables better control over brightness and contrast. Full-array LED TVs with local dimming can produce deeper blacks and more vibrant colors, enhancing the overall viewing experience. This capability is especially noticeable in dark scenes, where traditional LCD TVs might show washed-out blacks.
Moreover, LED TVs often support High Dynamic Range (HDR) content, which increases the range of colors and brightness levels, making images appear more lifelike. HDR compatibility has become a standard feature in mid-range and high-end LED TVs, catering to the growing demand for immersive viewing experiences.
Design and Form Factor
LED technology has enabled manufacturers to produce ultra-thin and lightweight TVs. Edge-lit LED TVs, in particular, can be as slim as a few millimeters, allowing for sleek designs that blend seamlessly into modern living spaces.
This slim profile also makes wall mounting easier and more aesthetically pleasing. The reduced weight compared to plasma or older LCD TVs means less strain on mounting hardware and more flexibility in placement.
Types of LED TVs: Edge-Lit vs. Full-Array
Edge-Lit LED TVs
Edge-lit LED TVs position the LEDs along the perimeter of the screen. Light is spread across the display using light guides and diffusers. This design allows for very thin panels and is generally more affordable to manufacture.
However, edge-lit TVs may suffer from uneven lighting, especially in scenes with high contrast. Light bleed or “clouding” can occur, where bright areas spill into darker zones, reducing picture quality. Despite this, many edge-lit models perform admirably for everyday viewing, particularly in well-lit rooms.
Full-Array LED TVs with Local Dimming
Full-array LED TVs feature a grid of LEDs directly behind the LCD panel. This arrangement allows for local dimming, where specific zones of LEDs can be dimmed or brightened independently. This technology significantly improves contrast ratios and black levels, making images more dynamic and realistic.
Full-array LED TVs tend to be thicker and more expensive than edge-lit models but offer superior picture quality. They are often favored by enthusiasts and those who prioritize cinematic viewing experiences.
Comparing LED TVs to Other Display Technologies
LED vs. OLED
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) TVs represent a different technology where each pixel emits its own light, eliminating the need for backlighting. This results in perfect black levels, infinite contrast ratios, and excellent viewing angles.
While OLED TVs generally offer superior picture quality, they tend to be more expensive and have a higher risk of burn-in, where static images can leave a permanent mark on the screen. LED TVs, especially full-array models, have narrowed the gap in picture quality and remain a more affordable and durable option for many consumers.
LED vs. QLED
QLED (Quantum Dot LED) TVs are essentially LED TVs enhanced with a quantum dot layer that improves color accuracy and brightness. Quantum dots are tiny semiconductor particles that emit precise colors when illuminated by the LED backlight.
QLED TVs can achieve higher peak brightness levels than standard LED TVs, making them excellent for bright rooms. They also tend to have longer lifespans and are less susceptible to burn-in compared to OLEDs. Many premium brands use QLED technology to offer a middle ground between LED and OLED performance.
LED vs. Plasma
Plasma TVs were once popular for their excellent color reproduction and deep blacks. However, they were bulky, consumed more power, and were prone to screen burn-in. Plasma production ceased around 2014, making LED TVs the dominant technology.
LED TVs offer better energy efficiency, thinner designs, and improved durability. While some enthusiasts still appreciate plasma’s picture quality, LED technology has largely surpassed it in all practical aspects.
Choosing the Right LED TV for Your Needs
Consider Your Viewing Environment
The lighting conditions in your room play a crucial role in determining the best TV type. For bright rooms with lots of ambient light, an LED TV with high brightness and anti-reflective coatings is ideal. Edge-lit LED TVs with good brightness can perform well here.
For darker rooms or home theaters, a full-array LED TV with local dimming will provide better contrast and deeper blacks, enhancing the cinematic experience.
Screen Size and Resolution
LED TVs come in a wide range of sizes, from compact 32-inch models to massive 85-inch screens. The ideal size depends on your room size and viewing distance. For example, a 55-inch TV is suitable for a typical living room with a viewing distance of about 7-9 feet.
Resolution is another vital factor. Most LED TVs today support 4K Ultra HD resolution, offering four times the pixels of Full HD. This higher resolution provides sharper images, especially on larger screens. Many models also support 8K resolution, but content availability remains limited.
Smart Features and Connectivity
Modern LED TVs often come equipped with smart platforms, allowing access to streaming services, apps, and voice assistants. When choosing a TV, consider the operating system and user interface, as well as the availability of apps you use regularly.
Connectivity options such as multiple HDMI ports, USB inputs, and support for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth are essential for integrating your TV with other devices like gaming consoles, soundbars, and media players.
Future Trends in LED TV Technology
Mini-LED and Micro-LED Innovations
Recent advancements have led to the development of Mini-LED and Micro-LED technologies, which represent the next generation of LED backlighting.
Mini-LED TVs use thousands of tiny LEDs for backlighting, allowing for even more precise local dimming and improved contrast compared to traditional full-array LED TVs. This technology offers a near-OLED level of picture quality while maintaining the brightness and durability advantages of LEDs.
Micro-LED technology takes this further by using microscopic LEDs as individual pixels, similar to OLED but without the organic components. Micro-LED promises perfect blacks, high brightness, and long lifespan, but it is currently very expensive and mainly found in commercial or luxury displays.
Enhanced HDR and Color Accuracy
As content creators continue to push the boundaries of visual storytelling, LED TVs are evolving to support wider color gamuts and higher dynamic ranges. Technologies such as Dolby Vision IQ and HDR10+ adapt HDR performance based on ambient lighting, offering a more consistent and immersive viewing experience.
Conclusion
LED TVs have revolutionized the television market by combining energy efficiency, improved picture quality, and sleek designs. Understanding the nuances of LED display technology—from edge-lit to full-array and the emerging Mini-LED innovations—empowers consumers to choose the right TV for their needs.
While OLED and QLED technologies offer compelling alternatives, LED TVs remain a versatile and accessible choice for most viewers. By considering factors such as viewing environment, screen size, resolution, and smart features, buyers can find an LED TV that delivers excellent performance and value for years to come.
Discover the Future of Visual Experience with LumenMatrix
Ready to elevate your viewing experience with the latest in LED display technology? LumenMatrix is at the forefront of innovation, offering an array of LED display solutions tailored to your unique needs. From captivating Indoor and Outdoor LED Wall Displays to dynamic Vehicle and Sports LED Displays, our products are designed to transform your visual communication and engagement. Explore our versatile range, including the sleek LED Poster Display, interactive Floor LED Displays, and the revolutionary All-in-One LED Display. Experience the difference with LumenMatrix and let your message shine with unmatched clarity and impact. Check out LumenMatrix LED Display Solutions today and join the visual revolution.